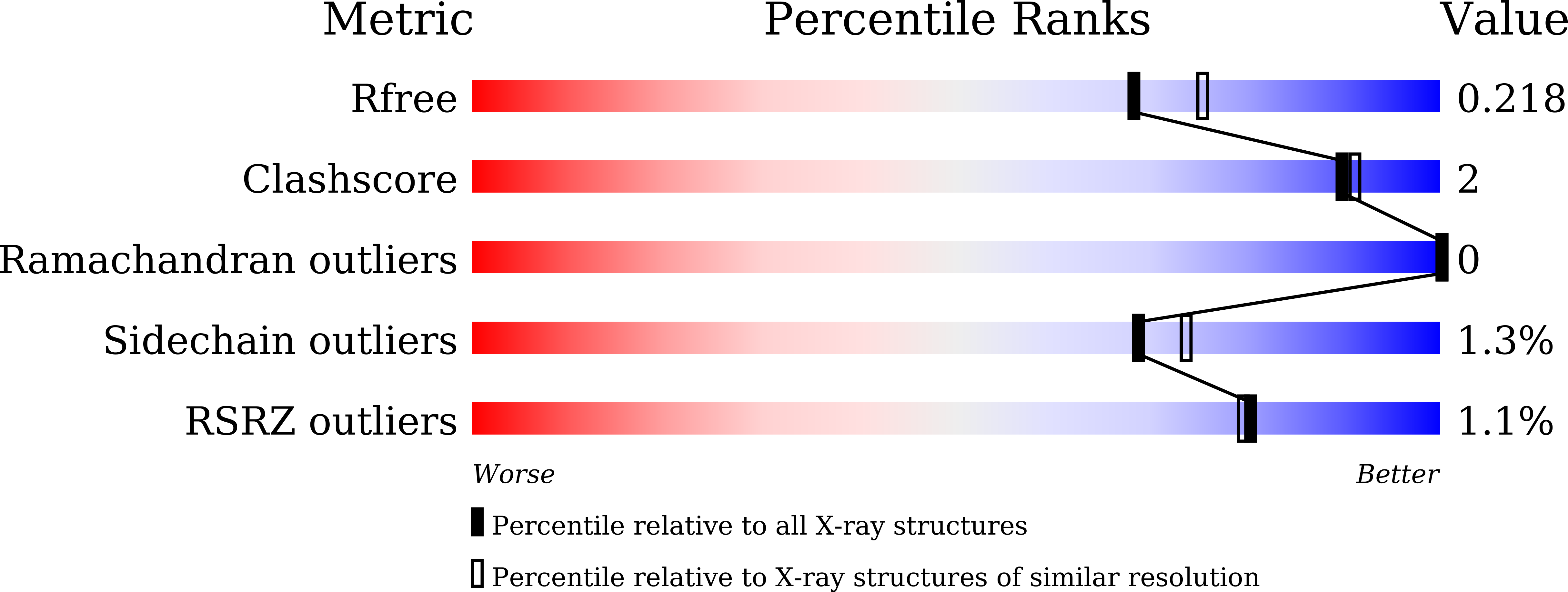
Structure of product-bound SMG1 lipase: active site gating implications.
Guo, S., Xu, J., Pavlidis, I.V., Lan, D., Bornscheuer, U.T., Liu, J., Wang, Y.(2015) FEBS J 282: 4538-4547
- PubMed: 26365206
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13513
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4ZRD, 4ZRE - PubMed Abstract:
Monoacylglycerol and diacylglycerol lipases are industrially interesting enzymes, due to the health benefits that arise from the consumption of diglycerides compared to the traditional triglyceride oils. Most lipases possess an α-helix (lid) directly over the catalytic pocket which regulates the activity of the enzyme. Generally, lipases exist in active and inactive conformations, depending on the positioning of this lid subdomain. However, lipase SMG1, a monoacylglycerol and diacylglycerol specific lipase, has an atypical activation mechanism. In the present study we were able to prove by crystallography, in silico analysis and activity tests that only two positions, residues 102 and 278, are responsible for a gating mechanism that regulates the active and inactive states of the lipase, and that no significant structural changes take place during activation except for oxyanion hole formation. The elucidation of the gating effect provided data enabling the rational design of improved lipases with 6-fold increase in the hydrolytic activity toward diacylglycerols, just by providing additional substrate stabilization with a single mutation (F278N or F278T). Due to the conservation of F278 among the monoacylglycerol and diacylglycerol lipases in the Rhizomucor miehei lipase-like family, the gating mechanism described herein might represent a general mechanism applicable to other monoacylglycerol and diacylglycerol lipases as well. Database: Structural data are available in the Protein Data Bank under the accession numbers 4ZRE (F278D mutant) and 4ZRD (F278N mutant).
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Light Industry and Food Science, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China.