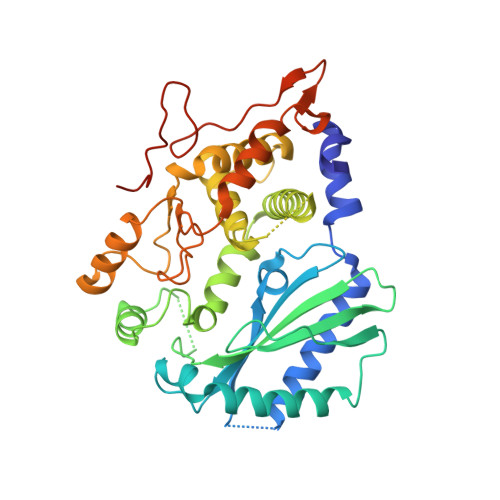
Structural mechanism of sensing long dsRNA via a noncatalytic domain in human oligoadenylate synthetase 3.
Donovan, J., Whitney, G., Rath, S., Korennykh, A.(2015) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112: 3949-3954
- PubMed: 25775560
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1419409112
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
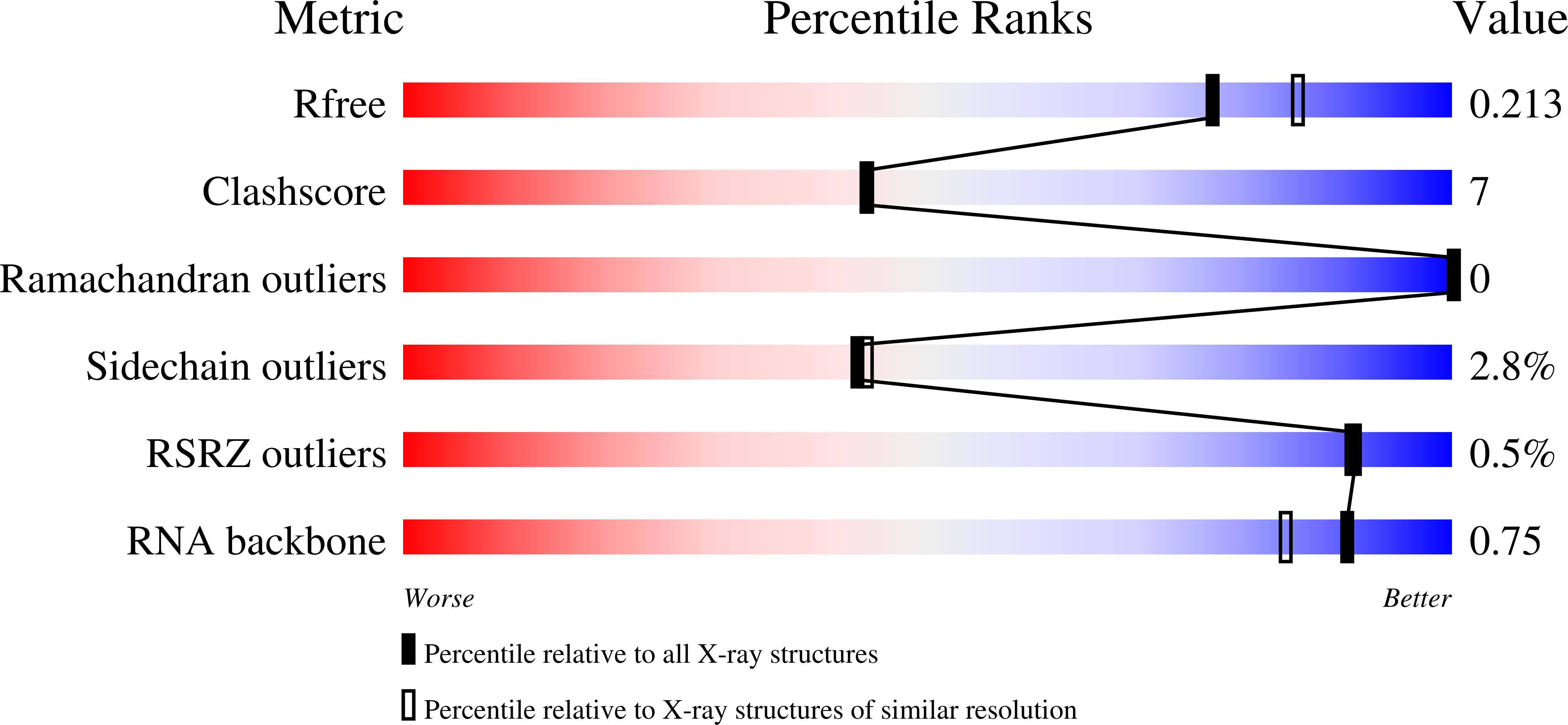
4S3N - PubMed Abstract:
The mammalian innate immune system uses several sensors of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) to develop the interferon response. Among these sensors are dsRNA-activated oligoadenylate synthetases (OAS), which produce signaling 2',5'-linked RNA molecules (2-5A) that activate regulated RNA decay in mammalian tissues. Different receptors from the OAS family contain one, two, or three copies of the 2-5A synthetase domain, which in several instances evolved into pseudoenzymes. The structures of the pseudoenzymatic domains and their roles in sensing dsRNA are unknown. Here we present the crystal structure of the first catalytically inactive domain of human OAS3 (hOAS3.DI) in complex with a 19-bp dsRNA, determined at 2.0-Å resolution. The conformation of hOAS3.DI is different from the apo- and the dsRNA-bound states of the catalytically active homolog, OAS1, reported previously. The unique conformation of hOAS3.DI disables 2-5A synthesis by placing the active site residues nonproductively, but favors the binding of dsRNA. Biochemical data show that hOAS3.DI is essential for activation of hOAS3 and serves as a dsRNA-binding module, whereas the C-terminal domain DIII carries out catalysis. The location of the dsRNA-binding domain (DI) and the catalytic domain (DIII) at the opposite protein termini makes hOAS3 selective for long dsRNA. This mechanism relies on the catalytic inactivity of domain DI, revealing a surprising role of pseudoenzyme evolution in dsRNA surveillance.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544.