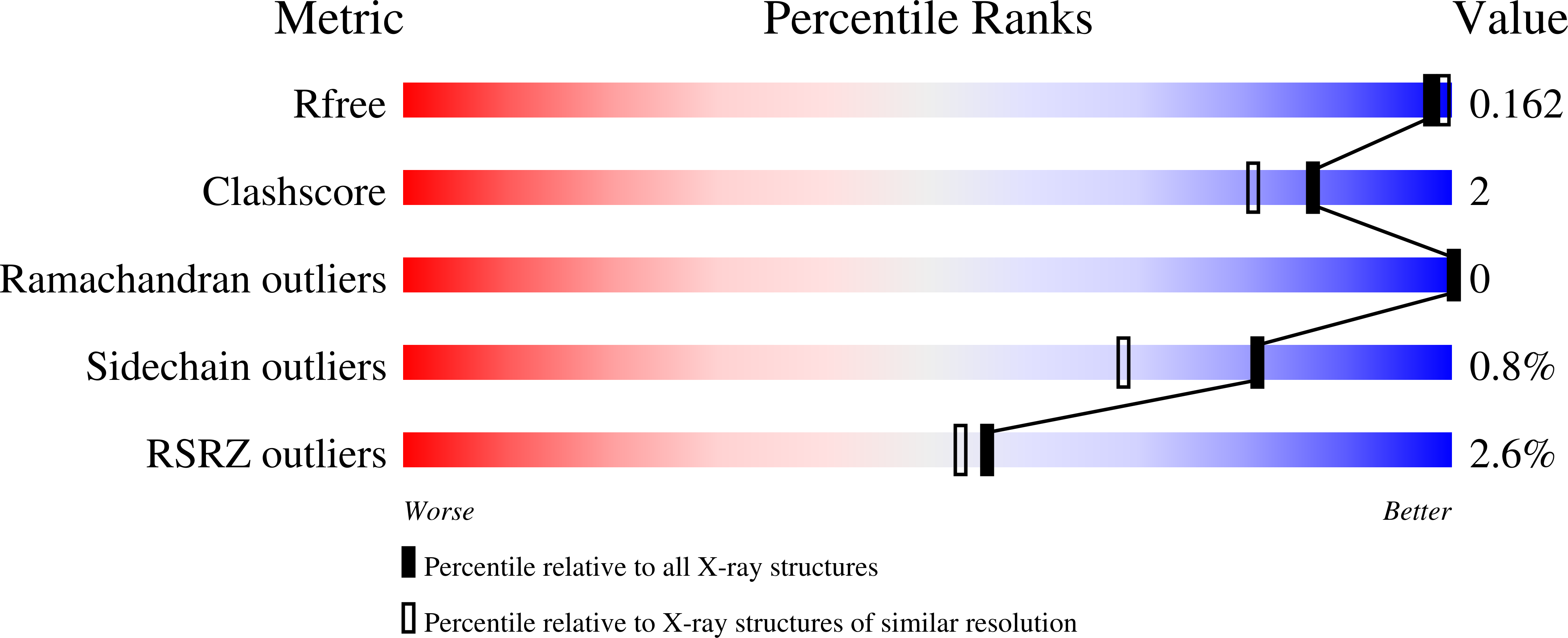
Crystal structures of GI.8 Boxer virus P dimers in complex with HBGAs, a novel evolutionary path selected by the Lewis epitope.
Hao, N., Chen, Y., Xia, M., Tan, M., Liu, W., Guan, X., Jiang, X., Li, X., Rao, Z.(2015) Protein Cell 6: 101-116
- PubMed: 25547362
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-014-0126-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4RDJ, 4RDK, 4RDL - PubMed Abstract:
Human noroviruses (huNoVs) recognize histo-blood group antigens (HBGAs) as attachment factors, in which genogroup (G) I and GII huNoVs use distinct binding interfaces. The genetic and evolutionary relationships of GII huNoVs under selection by the host HBGAs have been well elucidated via a number of structural studies; however, such relationships among GI NoVs remain less clear due to the fact that the structures of HBGA-binding interfaces of only three GI NoVs with similar binding profiles are known. In this study the crystal structures of the P dimers of a Lewis-binding strain, the GI.8 Boxer virus (BV) that does not bind the A and H antigens, in complex with the Lewis b (Le(b)) and Le(y) antigens, respectively, were determined and compared with those of the three previously known GI huNoVs, i.e. GI.1 Norwalk virus (NV), GI.2 FUV258 (FUV) and GI.7 TCH060 (TCH) that bind the A/H/Le antigens. The HBGA binding interface of BV is composed of a conserved central binding pocket (CBP) that interacts with the β-galactose of the precursor, and a well-developed Le epitope-binding site formed by five amino acids, including three consecutive residues from the long P-loop and one from the S-loop of the P1 subdomain, a feature that was not seen in the other GI NoVs. On the other hand, the H epitope/acetamido binding site observed in the other GI NoVs is greatly degenerated in BV. These data explain the evolutionary path of GI NoVs selected by the polymorphic human HBGAs. While the CBP is conserved, the regions surrounding the CBP are flexible, providing freedom for changes. The loss or degeneration of the H epitope/acetamido binding site and the reinforcement of the Le binding site of the GI.8 BV is a typical example of such change selected by the host Lewis epitope.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100101, China.