Structural Basis for Substrate-specific Acetylation of N alpha-acetyltransferase Ard1 from Sulfolobus solfataricus
Chang, Y.Y., Hsu, C.H.(2015) Sci Rep 5: 8673-8673
- PubMed: 25728374
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08673
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4R3K, 4R3L - PubMed Abstract:
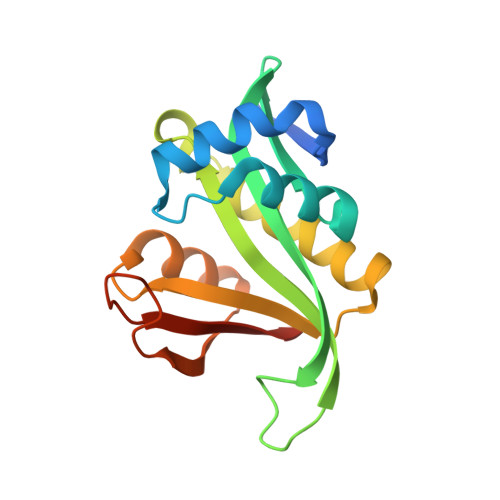
Nα-acetyltransferases (Nats) possess a wide range of important biological functions. Their structures can vary according to the first two residues of their substrate. However, the mechanisms of substrate recognition and catalysis of Nats are elusive. Here, we present two structure of Sulfolobus solfataricus Ard1 (SsArd1), a member of the NatA family, at 2.13 and 1.84 Å. Both structures contain coenzyme A, while the latter also contains a substrate-derived peptide. Sequential structure-based mutagenesis revealed that mutations of critical residues for CoA binding decreased the binding affinity of SsArd1 by 3 ~ 7-fold. Superimposition of SsArd1 (NatA) with human Naa50p (NatE) showed significant differences in key residues of enzymes near the first amino-acid position of the substrate peptide (Glu35 for SsArd1 and Val29 for Naa50p). Further enzyme activity assays revealed that the substrate specificity of SsArd1 could be altered from SSGTPT to MEEKVG by a range of Glu35 mutants. These studies provide not only a molecular elucidation of substrate recognition and specificity for the NatA family, but also insight into how members of the NAT family distinguish between amino acids at the substrate N-terminus from the ancient monomeric archaeal Ard1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Agricultural Chemistry, National Taiwan University, Taipei 10617, Taiwan.