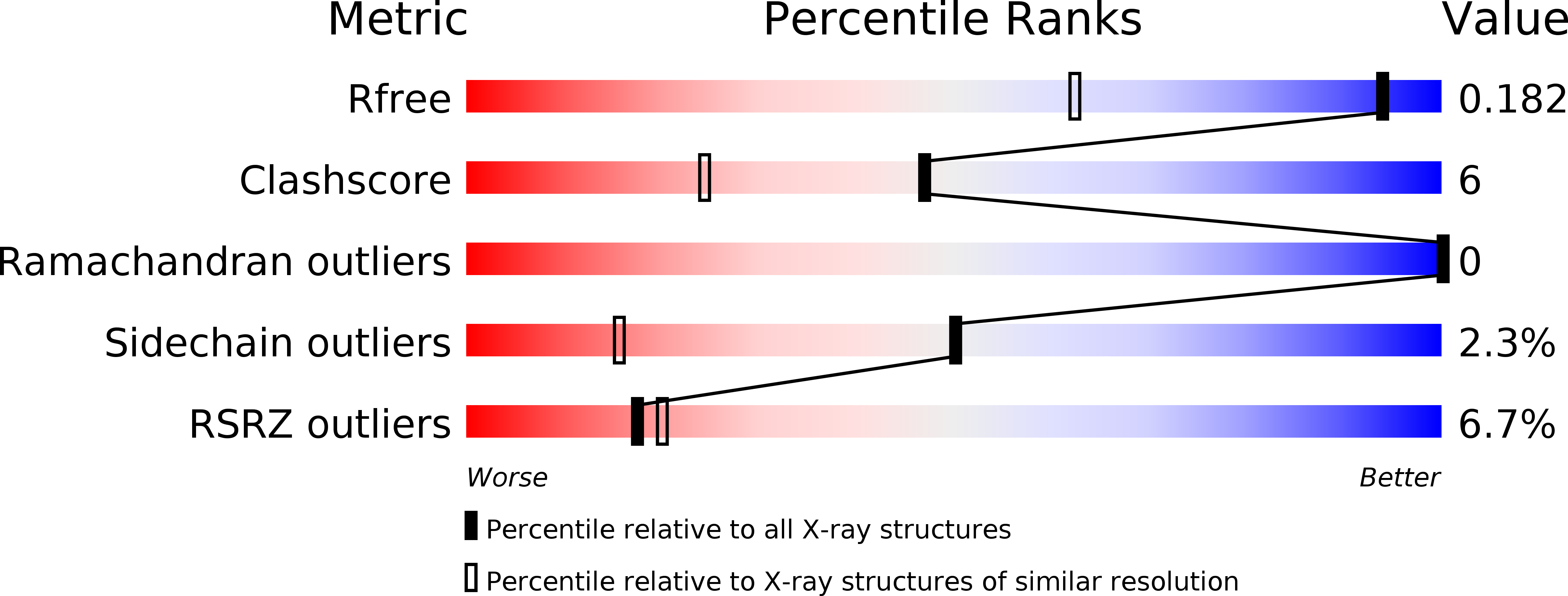
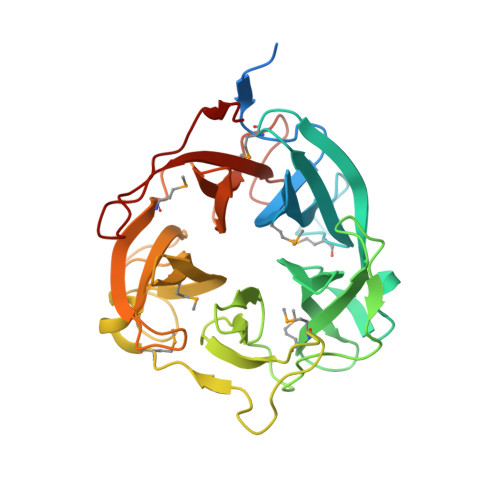
Structural analysis of the GH43 enzyme Xsa43E from Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus
Till, M., Goldstone, D., Card, G., Attwood, G.T., Moon, C.D., Arcus, V.L.(2014) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 70: 1193-1198
- PubMed: 25195890
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X14014745
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4NOV - PubMed Abstract:
The rumen of dairy cattle can be thought of as a large, stable fermentation vat and as such it houses a large and diverse community of microorganisms. The bacterium Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus is a representative of a significant component of this microbial community. It is a xylan-degrading organism whose genome encodes a large number of open reading frames annotated as fibre-degrading enzymes. This suite of enzymes is essential for the organism to utilize the plant material within the rumen as a fuel source, facilitating its survival in this competitive environment. Xsa43E, a GH43 enzyme from B. proteoclasticus, has been structurally and functionally characterized. Here, the structure of selenomethionine-derived Xsa43E determined to 1.3 Å resolution using single-wavelength anomalous diffraction is reported. Xsa43E possesses the characteristic five-bladed β-propeller domain seen in all GH43 enzymes. GH43 enzymes can have a range of functions, and the functional characterization of Xsa43E shows it to be an arabinofuranosidase capable of cleaving arabinose side chains from short segments of xylan. Full functional and structural characterization of xylan-degrading enzymes will aid in creating an enzyme cocktail that can be used to completely degrade plant material into simple sugars. These molecules have a range of applications as starting materials for many industrial processes, including renewable alternatives to fossil fuels.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Bristol, Bristol, England.