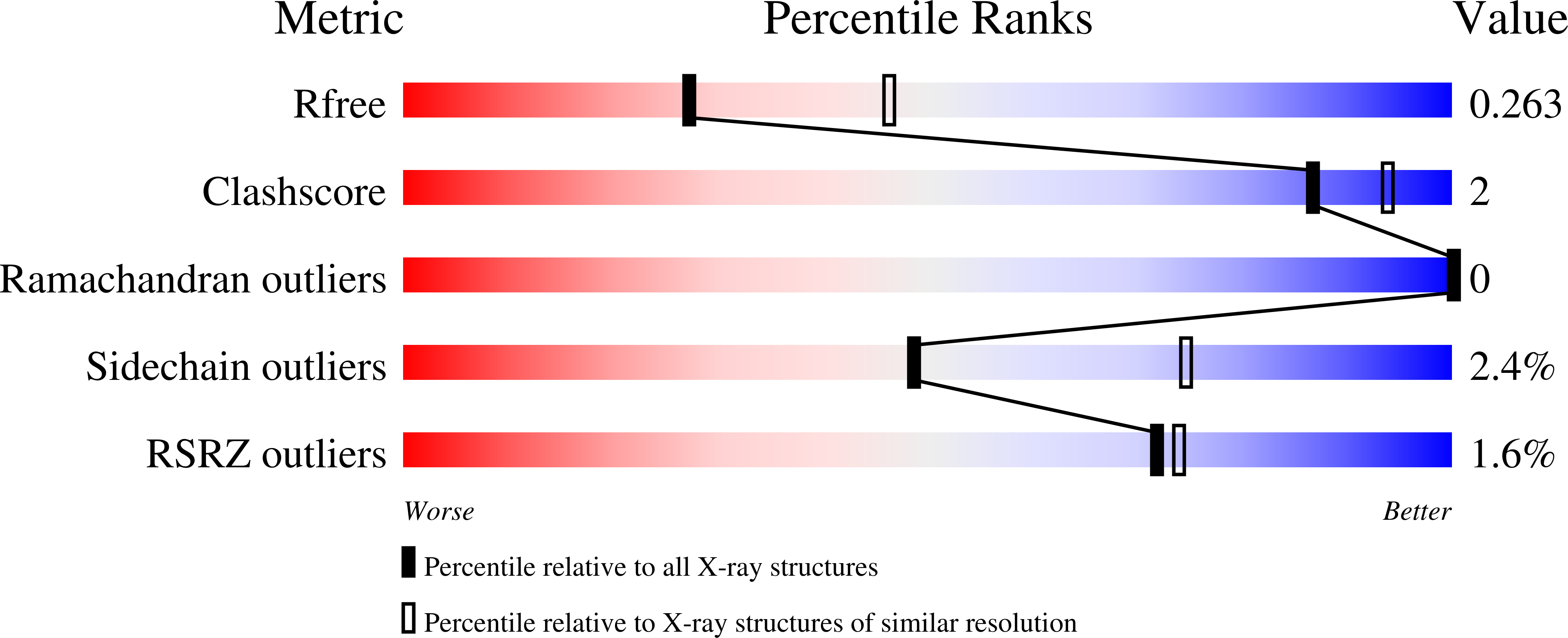
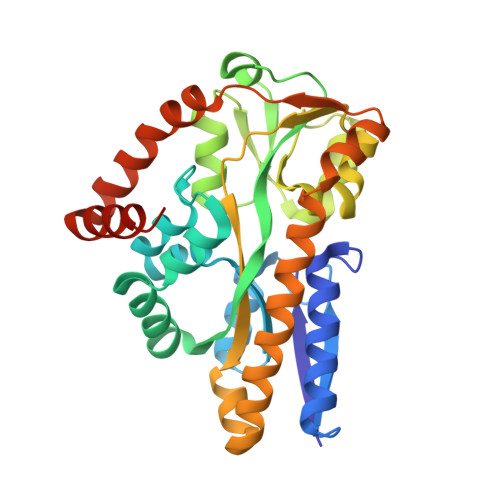
Bacterial periplasmic sialic acid-binding proteins exhibit a conserved binding site.
Gangi Setty, T., Cho, C., Govindappa, S., Apicella, M.A., Ramaswamy, S.(2014) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70: 1801-1811
- PubMed: 25004958
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S139900471400830X
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4MAG, 4MMP, 4MNP - PubMed Abstract:
Sialic acids are a family of related nine-carbon sugar acids that play important roles in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. These sialic acids are incorporated/decorated onto lipooligosaccharides as terminal sugars in multiple bacteria to evade the host immune system. Many pathogenic bacteria scavenge sialic acids from their host and use them for molecular mimicry. The first step of this process is the transport of sialic acid to the cytoplasm, which often takes place using a tripartite ATP-independent transport system consisting of a periplasmic binding protein and a membrane transporter. In this paper, the structural characterization of periplasmic binding proteins from the pathogenic bacteria Fusobacterium nucleatum, Pasteurella multocida and Vibrio cholerae and their thermodynamic characterization are reported. The binding affinities of several mutations in the Neu5Ac binding site of the Haemophilus influenzae protein are also reported. The structure and the thermodynamics of the binding of sugars suggest that all of these proteins have a very well conserved binding pocket and similar binding affinities. A significant conformational change occurs when these proteins bind the sugar. While the C1 carboxylate has been identified as the primary binding site, a second conserved hydrogen-bonding network is involved in the initiation and stabilization of the conformational states.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine, NCBS Campus, GKVK Post, Bangalore, Karnataka 560 065, India.