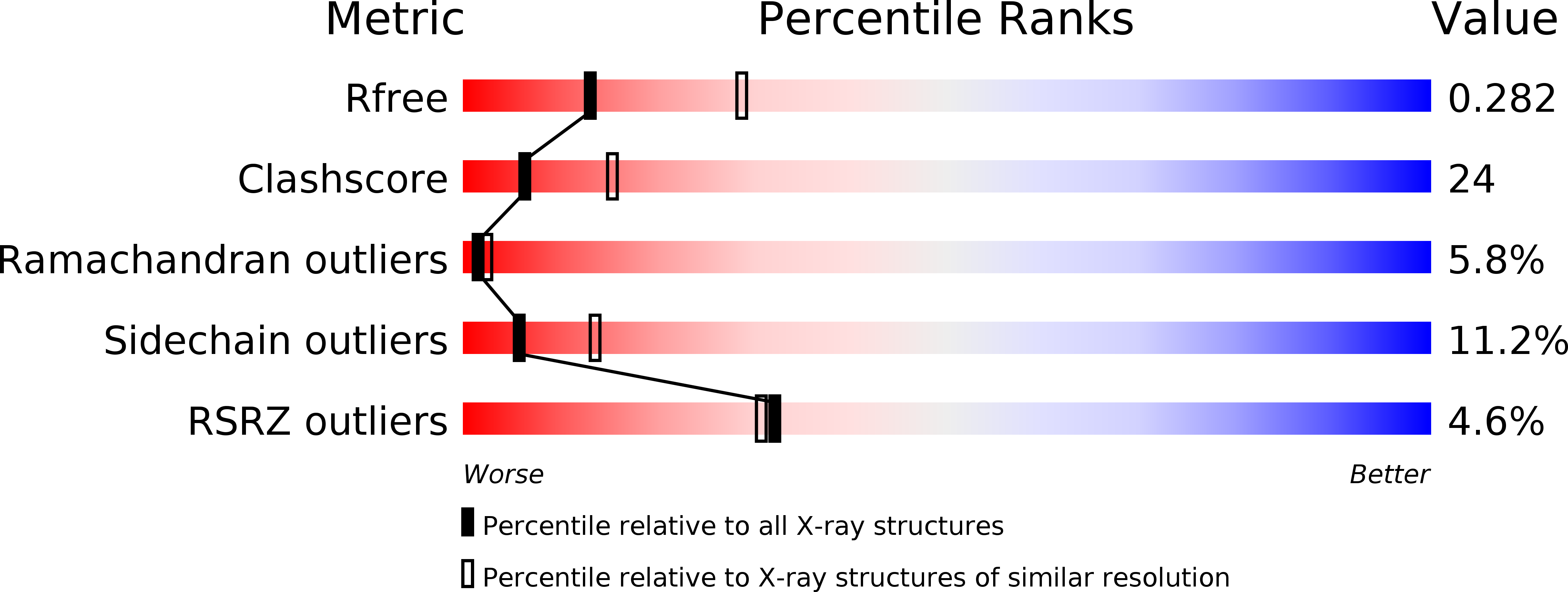
The N-Terminal Domain of PA from Bat-Derived Influenza-Like Virus H17N10 Has Endonuclease Activity
Tefsen, B., Lu, G., Zhu, Y., Haywood, J., Zhao, L., Deng, T., Qi, J., Gao, G.F.(2014) J Virol 88: 1935-1941
- PubMed: 24284327
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.03270-13
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4NFZ - PubMed Abstract:
Influenza imposes a great burden on society, not only in its seasonal appearance that affects both humans and domesticated animals but also through the constant threat of potential pandemics. Migratory birds are considered to be the reservoir hosts for influenza viruses, but other animals must also be considered. The recently identified influenza-like virus genome, from H17N10 in bats, was shown to be markedly different from genomes of other known influenza viruses, as both its surface glycoproteins hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) do not have canonical functions. However, no studies on other individual proteins from this particular virus have been reported until now. Here, we describe the structure of the N-terminal domain of PA from H17N10 influenza-like virus at 2.7-Å resolution and show that it has a fold similar to those of homologous PA domains present in more familiar influenza A virus strains. Moreover, we demonstrate that it possesses endonuclease activity and that the histidine residue in the active site is essential for this activity. Although this particular influenza virus subtype is probably not infectious for humans (even its virus state has not been confirmed in bats, as only the genome has been sequenced), reassortment of canonical influenza viruses with certain segments from H17N10 cannot be ruled out at this stage. Therefore, further studies are urgently needed for the sake of influenza prevention and control.
Organizational Affiliation:
CAS Key Laboratory of Pathogenic Microbiology and Immunology, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China.