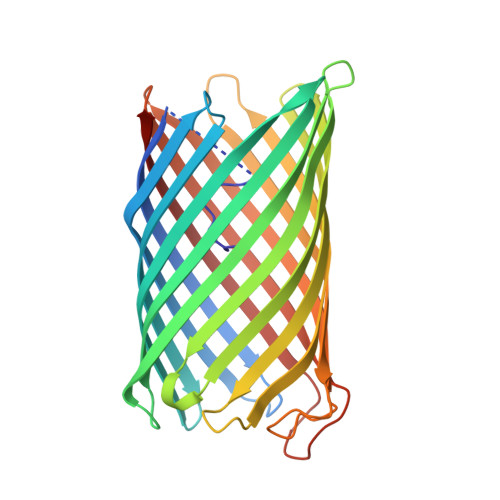
Outer-membrane translocation of bulky small molecules by passive diffusion.
van den Berg, B., Prathyusha Bhamidimarri, S., Dahyabhai Prajapati, J., Kleinekathofer, U., Winterhalter, M.(2015) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112: E2991-E2999
- PubMed: 26015567
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1424835112
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4D51, 4D5B, 4D5D, 4V3G, 4V3H - PubMed Abstract:
The outer membrane (OM) of gram-negative bacteria forms a protective layer around the cell that serves as a permeability barrier to prevent unrestricted access of noxious substances. The permeability barrier of the OM results partly from the limited pore diameters of OM diffusion channels. As a consequence, there is an "OM size-exclusion limit," and the uptake of bulky molecules with molecular masses of more than ∼ 600 Da is thought to be mediated by TonB-dependent, active transporters. Intriguingly, the OM protein CymA from Klebsiella oxytoca does not depend on TonB but nevertheless mediates efficient OM passage of cyclodextrins with diameters of up to ∼ 15 Å. Here we show, by using X-ray crystallography, molecular dynamics simulations, and single-channel electrophysiology, that CymA forms a monomeric 14-stranded β-barrel with a large pore that is occluded on the periplasmic side by the N-terminal 15 residues of the protein. Representing a previously unidentified paradigm in OM transport, CymA mediates the passive diffusion of bulky molecules via an elegant transport mechanism in which a mobile element formed by the N terminus acts as a ligand-expelled gate to preserve the permeability barrier of the OM.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Cell and Molecular Biosciences, The Medical School, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne NE2 4HH, United Kingdom; bert.van-den-berg@ncl.ac.uk.