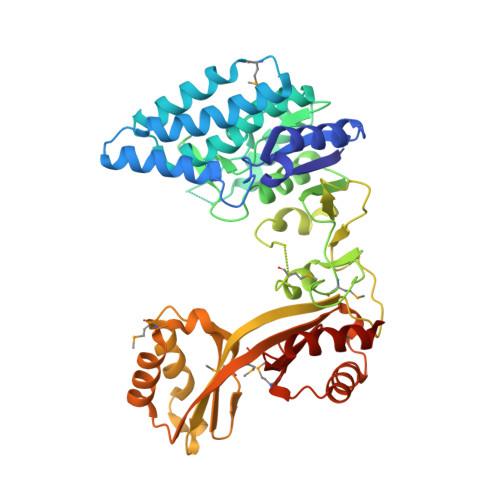
Crystal structure of Clostridium acetobutylicum Aspartate kinase (CaAK): An important allosteric enzyme for amino acids production.
Manjasetty, B.A., Chance, M.R., Burley, S.K., Panjikar, S., Almo, S.C.(2014) Biotechnol Rep (amst) 3: 73-85
- PubMed: 25170437
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2014.06.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3TVI - PubMed Abstract:
Aspartate kinase (AK) is an enzyme which is tightly regulated through feedback control and responsible for the synthesis of 4-phospho-L-aspartate from L-aspartate. This intermediate step is at an important branch point where one path leads to the synthesis of lysine and the other to threonine, methionine and isoleucine. Concerted feedback inhibition of AK is mediated by threonine and lysine and varies between the species. The crystal structure of biotechnologically important Clostridium acetobutylicum aspartate kinase ( Ca AK; E.C. 2.7.2.4; Mw =48,030Da; 437aa; SwissProt: Q97MC0) has been determined to 3Å resolution. Ca AK acquires a protein fold similar to the other known structures of AKs despite the low sequence identity (<30%). It is composed of two domains: an N-terminal catalytic domain (kinase) domain and a C-terminal regulatory domain further comprised of two small domains belonging to the ACT domain family. Pairwise comparison of 12 molecules in the asymmetric unit helped to identify the bending regions which are in the vicinity of ATP binding site involved in domain movements between the catalytic and regulatory domains. All 12 Ca AK molecules adopt fully open T-state conformation leading to the formation of three tetramers unique among other similar AK structures. On the basis of comparative structural analysis, we discuss tetramer formation based on the large conformational changes in the catalytic domain associated with the lysine binding at the regulatory domains. The structure described herein is homologous to a target in wide-spread pathogenic (toxin producing) bacteria such as Clostridium tetani (64% sequence identity) suggesting the potential of the structure solved here to be applied for modeling drug interactions. Ca AK structure may serve as a guide to better understand and engineer lysine biosynthesis for the biotechnology industry.