Crystal structure of the hexachlorocyclohexane dehydrochlorinase (LinA-type2): mutational analysis, thermostability and enantioselectivity
Macwan, A.S., Kukshal, V., Srivastava, N., Javed, S., Kumar, A., Ramachandran, R.(2012) PLoS One 7: e50373-e50373
- PubMed: 23209726
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050373
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
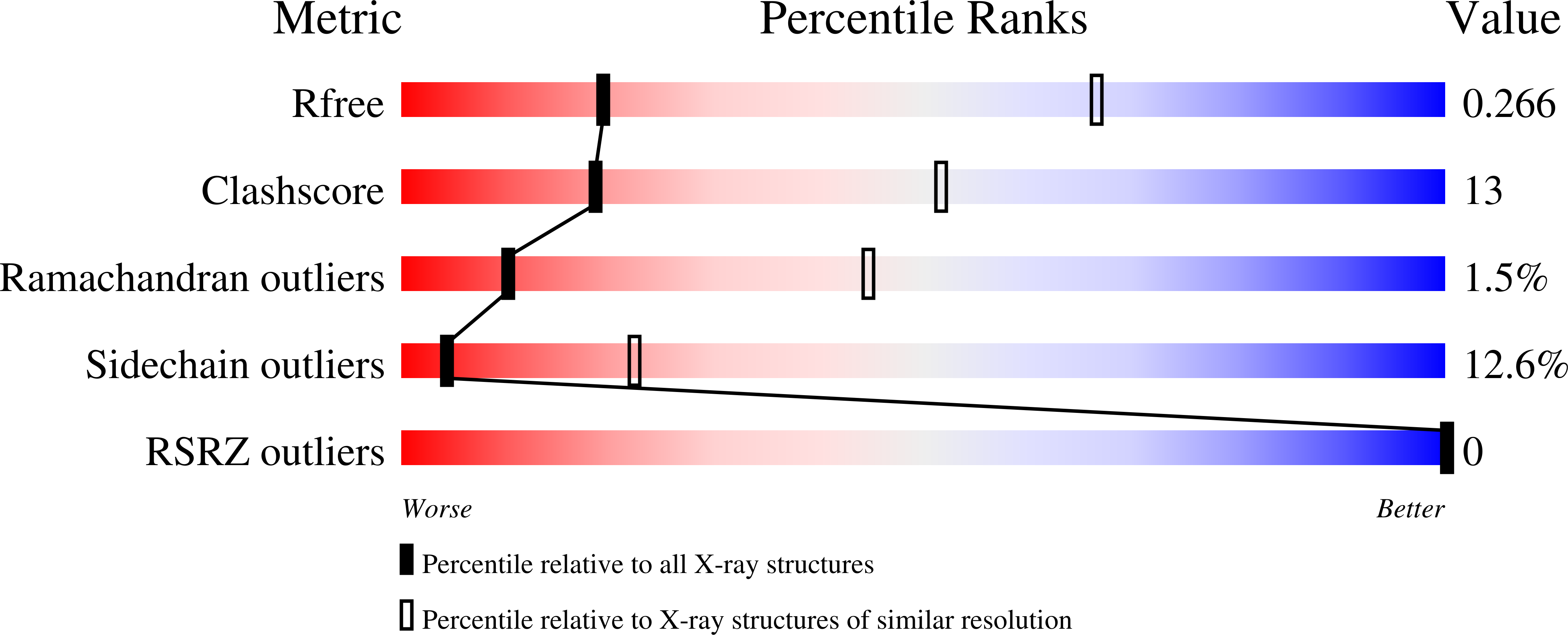
3S5C - PubMed Abstract:
Hexachlorocyclohexane dehydrochlorinase (LinA) mediates dehydrochlorination of γ-HCH to 1, 3, 4, 6-tetrachloro-1,4-cyclohexadiene that constitutes first step of the aerobic degradation pathway. We report the 3.5 Å crystal structure of a thermostable LinA-type2 protein, obtained from a soil metagenome, in the hexagonal space group P6(3)22 with unit cell parameters a = b = 162.5, c = 186.3 Å, respectively. The structure was solved by molecular replacement using the co-ordinates of LinA-type1 that exhibits mesophile-like properties. Structural comparison of LinA-type2 and -type1 proteins suggests that thermostability of LinA-type2 might partly arise due to presence of higher number of ionic interactions, along with 4% increase in the intersubunit buried surface area. Mutational analysis involving the differing residues between the -type1 and -type2 proteins, circular dichroism experiments and functional assays suggest that Q20 and G23 are determinants of stability for LinA-type2. It was earlier reported that LinA-type1 exhibits enantioselectivity for the (-) enantiomer of α-HCH. Contrastingly, we identified that -type2 protein prefers the (+) enantiomer of α-HCH. Structural analysis and molecular docking experiments suggest that changed residues K20Q, L96C and A131G, vicinal to the active site are probably responsible for the altered enantioselectivity of LinA-type2. Overall the study has identified features responsible for the thermostability and enantioselectivity of LinA-type2 that can be exploited for the design of variants for specific biotechnological applications.
Organizational Affiliation:
Environmental Biotechnology Division, CSIR-Indian Institute of Toxicology Research, Mahatma Gandhi Marg, Lucknow, India.