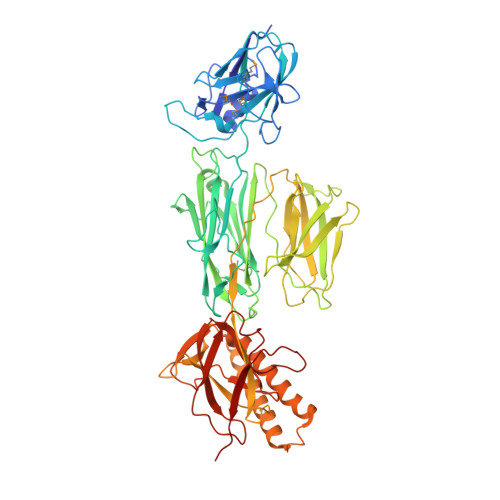
Structure of the Full-Length Major Pilin from Streptococcus pneumoniae: Implications for Isopeptide Bond Formation in Gram-Positive Bacterial Pili
Paterson, N.G., Baker, E.N.(2011) PLoS One 6: e22095-e22095
- PubMed: 21760959
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0022095
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3RPK - PubMed Abstract:
The surface of the pneumococcal cell is adorned with virulence factors including pili. The major pilin RrgB, which forms the pilus shaft on pathogenic Streptococcus pneumoniae, comprises four immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains, each with a common CnaB topology. The three C-terminal domains are each stabilized by internal Lys-Asn isopeptide bonds, formed autocatalytically with the aid of an essential Glu residue. The structure and orientation of the crucial N-terminal domain, which provides the covalent linkage to the next pilin subunit in the shaft, however, remain incompletely characterised. We report the crystal structure of full length RrgB, solved by X-ray crystallography at 2.8 Å resolution. The N-terminal (D1) domain makes few contacts with the rest of the RrgB structure, and has higher B-factors. This may explain why D1 is readily lost by proteolysis, as are the N-terminal domains of many major pilins. D1 is also found to have a triad of Lys, Asn and Glu residues in the same topological positions as in the other domains, yet mass spectrometry and the crystal structure show that no internal isopeptide bond is formed. We show that this is because β-strand G of D1, which carries the Asn residue, diverges from β-strand A, carrying the Lys residue, such that these residues are too far apart for bond formation. Strand G also carries the YPKN motif that provides the essential Lys residue for the sortase-mediated intermolecular linkages along the pilus shaft. Interaction with the sortase and formation of the intermolecular linkage could result in a change in the orientation of this strand, explaining why isopeptide bond formation in the N-terminal domains of some major pilins appears to take place only upon assembly of the pili.
Organizational Affiliation:
Maurice Wilkins Centre for Molecular Biodiscovery and School of Biological Sciences, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand.