Kinetic and structural analysis of substrate specificity in two copper amine oxidases from Hansenula polymorpha.
Chang, C.M., Klema, V.J., Johnson, B.J., Mure, M., Klinman, J.P., Wilmot, C.M.(2010) Biochemistry 49: 2540-2550
- PubMed: 20155950
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi901933d
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3LOY - PubMed Abstract:
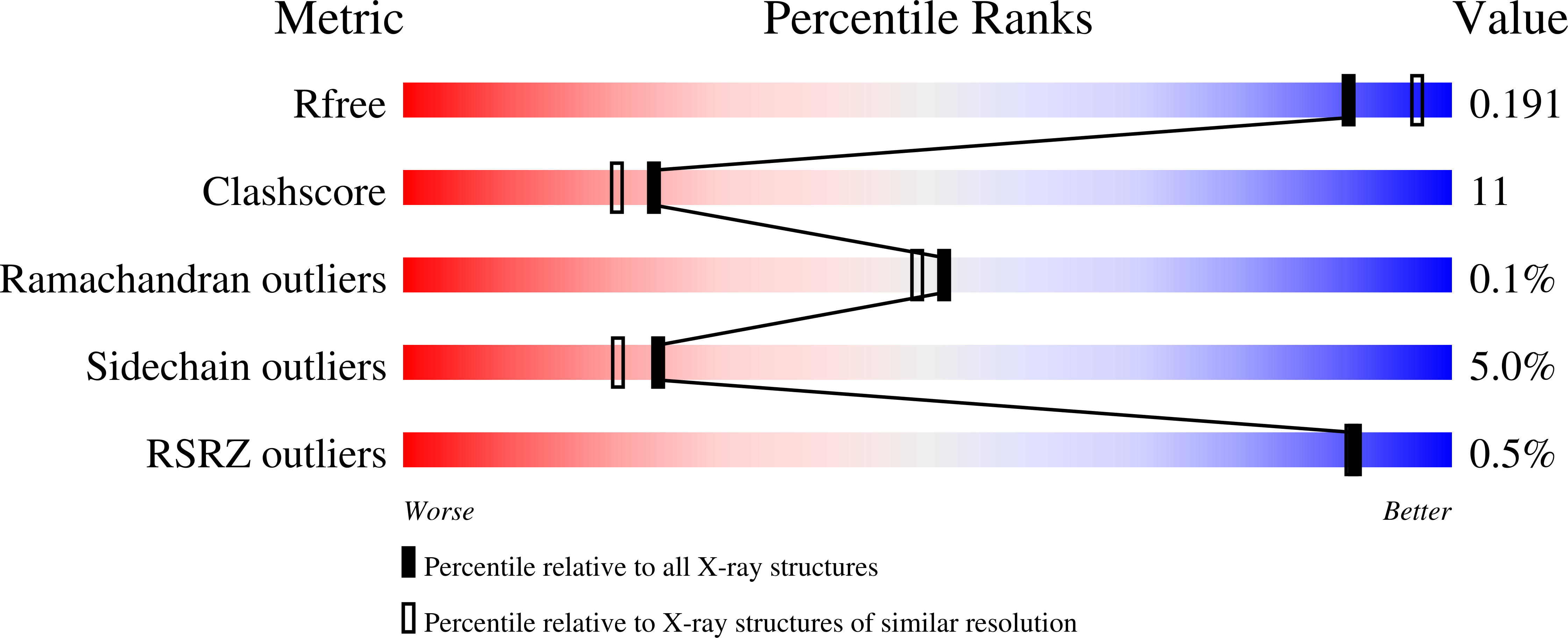
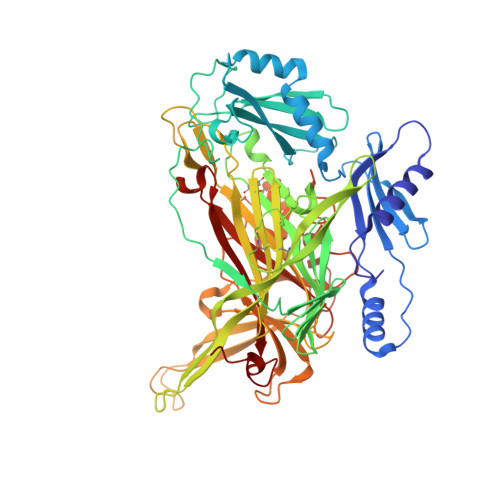
The structural underpinnings of enzyme substrate specificity are investigated in a pair of copper amine oxidases (CAOs) from Hansenula polymorpha (HPAO-1 and HPAO-2). The X-ray crystal structure (to 2.0 A resolution) and steady state kinetic data of the second copper amine oxidase (HPAO-2) are presented for comparison to those of HPAO-1. Despite 34% sequence identity and superimposable active site residues implicated in catalysis, the enzymes vary considerably in their substrate entry channel. The previously studied CAO, HPAO-1, has a narrow substrate channel. In contrast, HPAO-2 has a wide funnel-shaped substrate channel, which also contains a side chamber. In addition, there are a number of amino acid changes within the channels of HPAO-2 and HPAO-1 that may sterically impact the ability of substrates to form covalent Schiff base catalytic intermediates and to initiate chemistry. These differences can partially explain the greatly different substrate specificities as characterized by k(cat)/K(m) value differences. In HPAO-1, the k(cat)/K(m) for methylamine is 330-fold greater than for benzylamine, whereas in HPAO-2, it is benzylamine that is the better substrate by 750-fold. In HPAO-2, an inflated (D)k(cat)/K(m)(methylamine) in relation to (D)k(cat)/K(m)(benzylamine) indicates that proton abstraction has been impeded more than substrate release. In HPAO-1, (D)k(cat)/K(m)(S) changes little with the slow substrate and indicates a similar increase in the energy barriers that control both substrate binding and subsequent catalysis. In neither case is k(cat)/K(m) for the second substrate, O(2), significantly altered. These results reinforce the modular nature of the active sites of CAOs and show that multiple factors contribute to substrate specificity and catalytic efficiency. In HPAO-1, the enzyme with the smaller substrate binding pocket, both initial substrate binding and proton loss are affected by an increase in substrate size, while in HPAO-2, the enzyme with the larger substrate binding pocket, the rate of proton loss is differentially affected when a phenyl substituent in the substrate is reduced to the size of a methyl group.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720, USA.