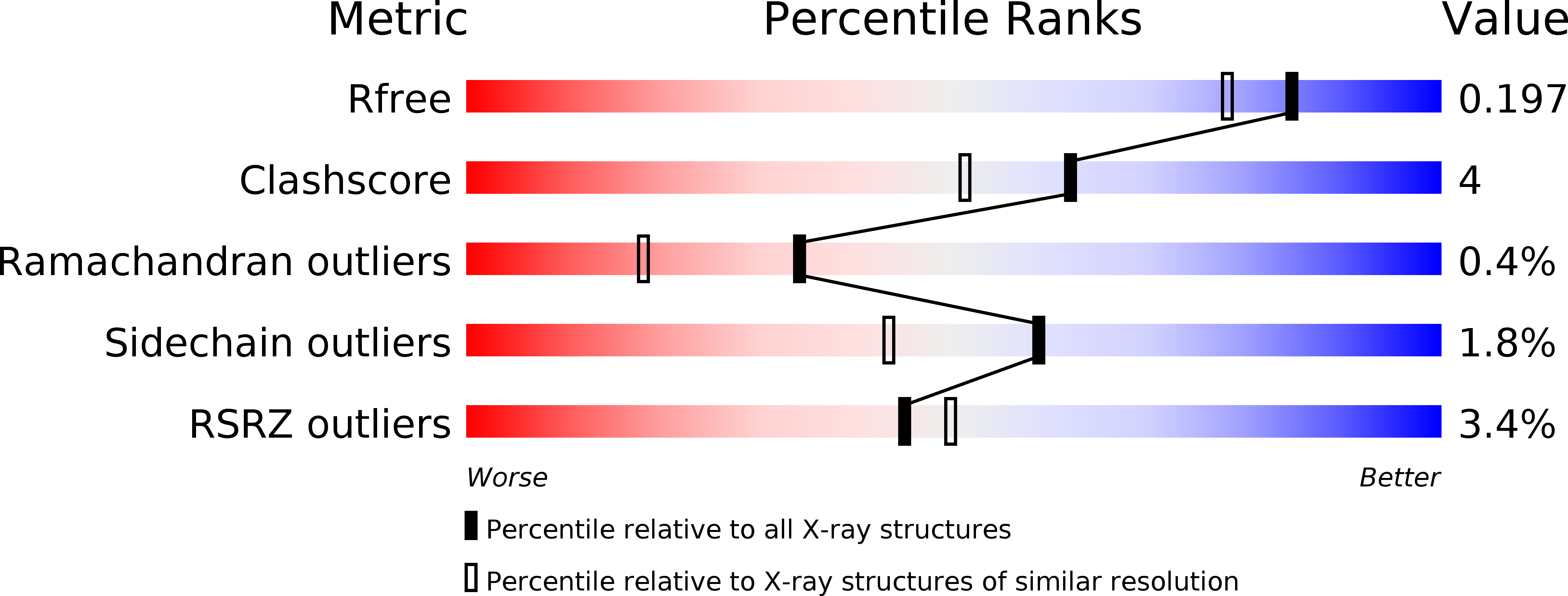
Structure and function of an iterative polyketide synthase thioesterase domain catalyzing Claisen cyclization in aflatoxin biosynthesis.
Korman, T.P., Crawford, J.M., Labonte, J.W., Newman, A.G., Wong, J., Townsend, C.A., Tsai, S.C.(2010) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107: 6246-6251
- PubMed: 20332208
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0913531107
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ILS - PubMed Abstract:
Polyketide natural products possess diverse architectures and biological functions and share a subset of biosynthetic steps with fatty acid synthesis. The final transformation catalyzed by both polyketide synthases (PKSs) and fatty acid synthases is most often carried out by a thioesterase (TE). The synthetic versatility of TE domains in fungal nonreducing, iterative PKSs (NR-PKSs) has been shown to extend to Claisen cyclase (CLC) chemistry by catalyzing C-C ring closure reactions as opposed to thioester hydrolysis or O-C/N-C macrocyclization observed in previously reported TE structures. Catalysis of C-C bond formation as a product release mechanism dramatically expands the synthetic potential of PKSs, but how this activity was acquired has remained a mystery. We report the biochemical and structural analyses of the TE/CLC domain in polyketide synthase A, the multidomain PKS central to the biosynthesis of aflatoxin B(1), a potent environmental carcinogen. Mutagenesis experiments confirm the predicted identity of the catalytic triad and its role in catalyzing the final Claisen-type cyclization to the aflatoxin precursor, norsolorinic acid anthrone. The 1.7 A crystal structure displays an alpha/beta-hydrolase fold in the catalytic closed form with a distinct hydrophobic substrate-binding chamber. We propose that a key rotation of the substrate side chain coupled to a protein conformational change from the open to closed form spatially governs substrate positioning and C-C cyclization. The biochemical studies, the 1.7 A crystal structure of the TE/CLC domain, and intermediate modeling afford the first mechanistic insights into this widely distributed C-C bond-forming class of TEs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, University of California, Irvine, CA 92697, USA.