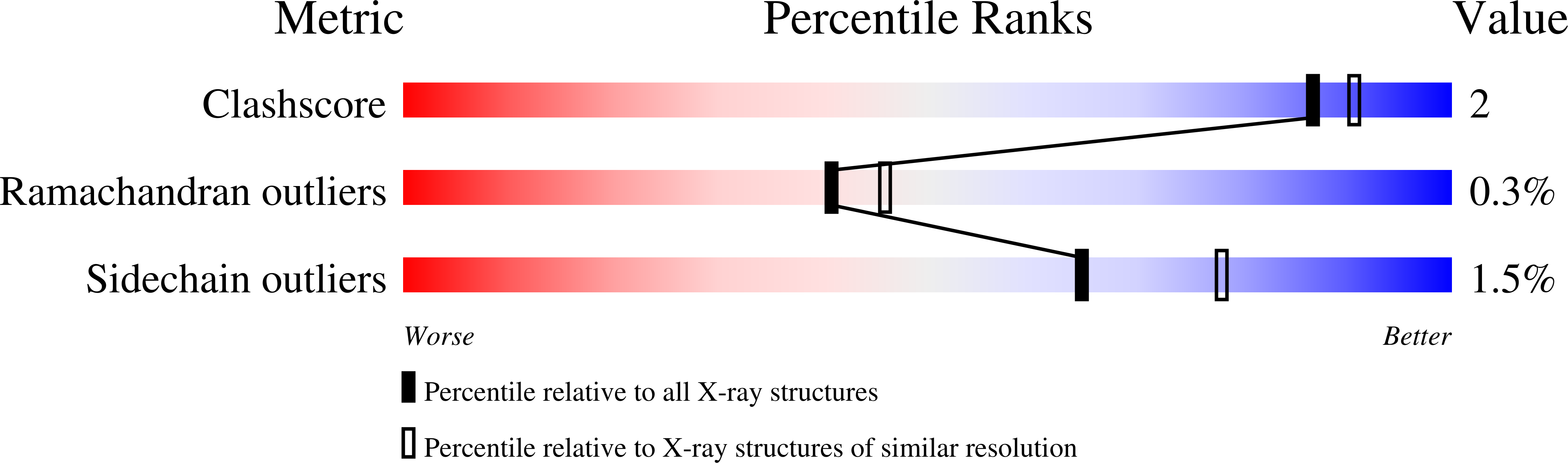
Rapid determination of hydrogen positions and protonation states of diisopropyl fluorophosphatase by joint neutron and X-ray diffraction refinement.
Blum, M.M., Mustyakimov, M., Ruterjans, H., Kehe, K., Schoenborn, B.P., Langan, P., Chen, J.C.(2009) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 713-718
- PubMed: 19136630
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0807842106
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3BYC - PubMed Abstract:
Hydrogen atoms constitute about half of all atoms in proteins and play a critical role in enzyme mechanisms and macromolecular and solvent structure. Hydrogen atom positions can readily be determined by neutron diffraction, and as such, neutron diffraction is an invaluable tool for elucidating molecular mechanisms. Joint refinement of neutron and X-ray diffraction data can lead to improved models compared with the use of neutron data alone and has now been incorporated into modern, maximum-likelihood based crystallographic refinement programs like CNS. Joint refinement has been applied to neutron and X-ray diffraction data collected on crystals of diisopropyl fluorophosphatase (DFPase), a calcium-dependent phosphotriesterase capable of detoxifying organophosphorus nerve agents. Neutron omit maps reveal a number of important features pertaining to the mechanism of DFPase. Solvent molecule W33, coordinating the catalytic calcium, is a water molecule in a strained coordination environment, and not a hydroxide. The smallest Ca-O-H angle is 53 degrees, well beyond the smallest angles previously observed. Residue Asp-229, is deprotonated, supporting a mechanism involving nucleophilic attack by Asp-229, and excluding water activation by the catalytic calcium. The extended network of hydrogen bonding interactions in the central water filled tunnel of DFPase is revealed, showing that internal solvent molecules form an important, integrated part of the overall structure.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biophysical Chemistry, Goethe University Frankfurt, Max-von-Laue-Strasse 9, 60438 Frankfurt, Germany.