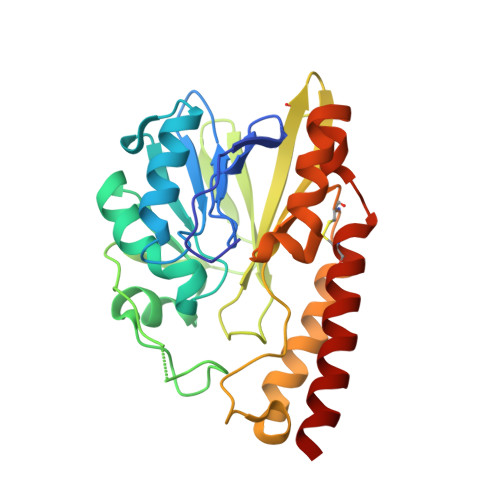
Structural Insights into the Subclass B3 Metallo-beta-Lactamase SMB-1 and the Mode of Inhibition by the Common Metallo- -Lactamase Inhibitor Mercaptoacetate
Wachino, J., Yamaguchi, Y., Mori, S., Kurosaki, H., Arakawa, Y., Shibayama, K.(2013) Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57: 101-109
- PubMed: 23070156
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01264-12
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3VPE, 3VQZ - PubMed Abstract:
A novel subclass B3 metallo-β-lactamase (MBL), SMB-1, recently identified from a Serratia marcescens clinical isolate, showed a higher hydrolytic activity against a wide range of β-lactams than did the other subclass B3 MBLs, i.e., BJP-1 and FEZ-1, from environmental bacteria. To identify the mechanism underlying the differences in substrate specificity among the subclass B3 MBLs, we determined the structure of SMB-1, using 1.6-Å diffraction data. Consequently, we found that SMB-1 reserves a space in the active site to accommodate β-lactam, even with a bulky R1 side chain, due to a loss of amino acid residues corresponding to F31 and L226 of BJP-1, which protrude into the active site to prevent β-lactam from binding. The protein also possesses a unique amino acid residue, Q157, which probably plays a role in recognition of β-lactams via the hydrogen bond interaction, which is missing in BJP-1 and FEZ-1, whose K(m) values for β-lactams are particularly high. In addition, we determined the mercaptoacetate (MCR)-complexed SMB-1 structure and revealed the mode of its inhibition by MCR: the thiolate group bridges to two zinc ions (Zn1 and Zn2). One of the carboxylate oxygen atoms of MCR makes contact with Zn2 and Ser221, and the other makes contact with T223 and a water molecule. Our results demonstrate the possibility that MCR could be a potent inhibitor for subclass B3 MBLs and that the screening technique using MCR as an inhibitor would be effective for detecting subclass B3 MBL producers.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Bacteriology II, National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Musashi-Murayama, Tokyo, Japan. wachino@nih.go.jp