Cellular Functions and X-ray Structure of Anthrolysin O, a Cholesterol-dependent Cytolysin Secreted by Bacillus anthracis
Bourdeau, R.W., Malito, E., Chenal, A., Bishop, B.L., Musch, M.W., Villereal, M.L., Chang, E.B., Mosser, E.M., Rest, R.F., Tang, W.J.(2009) J Biol Chem 284: 14645-14656
- PubMed: 19307185
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M807631200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3CQF - PubMed Abstract:
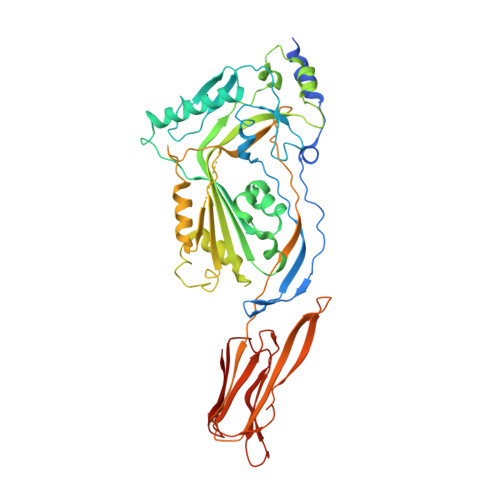
Anthrolysin O (ALO) is a pore-forming, cholesterol-dependent cytolysin (CDC) secreted by Bacillus anthracis, the etiologic agent for anthrax. Growing evidence suggests the involvement of ALO in anthrax pathogenesis. Here, we show that the apical application of ALO decreases the barrier function of human polarized epithelial cells as well as increases intracellular calcium and the internalization of the tight junction protein occludin. Using pharmacological agents, we also found that barrier function disruption requires increased intracellular calcium and protein degradation. We also report a crystal structure of the soluble state of ALO. Based on our analytical ultracentrifugation and light scattering studies, ALO exists as a monomer. Our ALO structure provides the molecular basis as to how ALO is locked in a monomeric state, in contrast to other CDCs that undergo antiparallel dimerization or higher order oligomerization in solution. ALO has four domains and is globally similar to perfringolysin O (PFO) and intermedilysin (ILY), yet the highly conserved undecapeptide region in domain 4 (D4) adopts a completely different conformation in all three CDCs. Consistent with the differences within D4 and at the D2-D4 interface, we found that ALO D4 plays a key role in affecting the barrier function of C2BBE cells, whereas PFO domain 4 cannot substitute for this role. Novel structural elements and unique cellular functions of ALO revealed by our studies provide new insight into the molecular basis for the diverse nature of the CDC family.
Organizational Affiliation:
Ben-May Department for Cancer Research, University of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois 60637, USA.