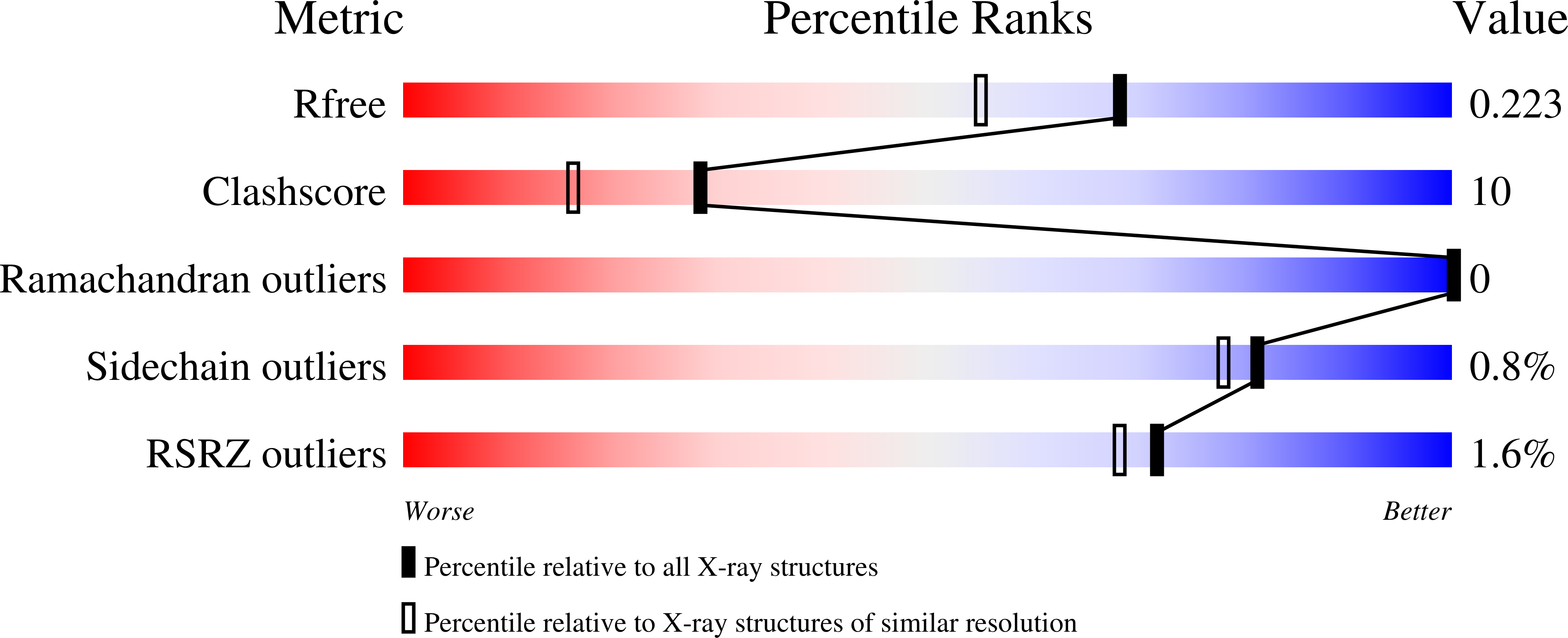
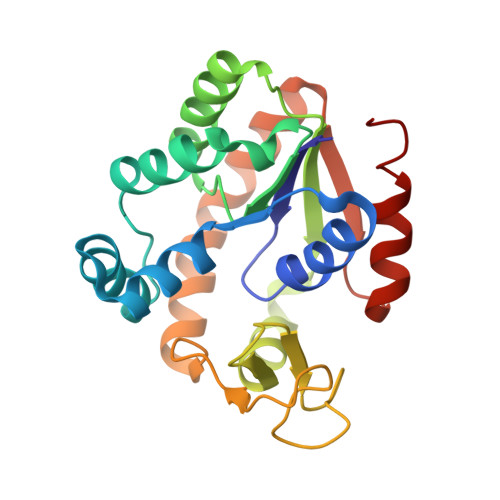
In vivo molecular evolution reveals biophysical origins of organismal fitness.
Counago, R., Chen, S., Shamoo, Y.(2006) Mol Cell 22: 441-449
- PubMed: 16713575
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2006.04.012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2EU8 - PubMed Abstract:
In nature, evolution occurs through the continuous adaptation of a population to its environment. At the molecular level, adaptive changes in protein sequence and expression impact organismal fitness and, consequently, dictate population dynamics. Here, we have used a "weak link" method to favor variations in one gene, allowing adaptation to thermostability to be studied in molecular detail as bacteria were grown continuously for approximately 1500 generations. Surprisingly, only six mutant alleles, representing less than 1% of the possible missense mutations, were observed, suggesting a highly constrained molecular landscape during protein evolution. The changes in organismal fitness were linked directly to incremental increases in enzyme stability and activity maxima and corresponded to the narrow temperature ranges where each mutant enjoyed success within the overall population. Thus, continuous evolution of a single gene permits a quantitative approach that extends from the phenotypes of the microbial populations to their underlying biophysical basis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Rice University, Houston, Texas 77005, USA.