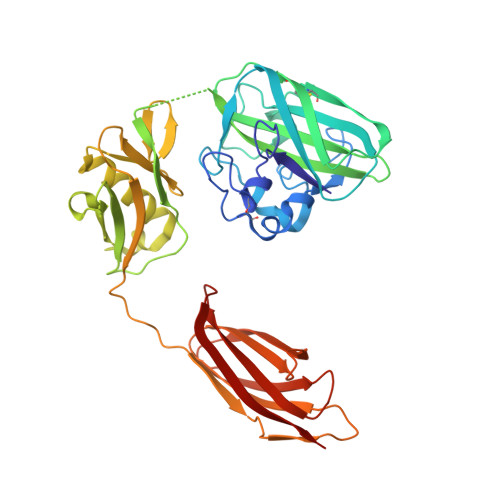
The Vibrio Cholerae Colonization Factor Gbpa Possesses a Modular Structure that Governs Binding to Different Host Surfaces.
Wong, E., Vaaje-Kolstad, G., Ghosh, A., Hurtado-Guerrero, R., Konarev, P.V., Ibrahim, A.F.M., Svergun, D.I., Eijsink, V.G.H., Chatterjee, N.S., Van Aalten, D.M.F.(2012) PLoS Pathog 8: 2373
- PubMed: 22253590
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002373
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2XWX - PubMed Abstract:
Vibrio cholerae is a bacterial pathogen that colonizes the chitinous exoskeleton of zooplankton as well as the human gastrointestinal tract. Colonization of these different niches involves an N-acetylglucosamine binding protein (GbpA) that has been reported to mediate bacterial attachment to both marine chitin and mammalian intestinal mucin through an unknown molecular mechanism. We report structural studies that reveal that GbpA possesses an unusual, elongated, four-domain structure, with domains 1 and 4 showing structural homology to chitin binding domains. A glycan screen revealed that GbpA binds to GlcNAc oligosaccharides. Structure-guided GbpA truncation mutants show that domains 1 and 4 of GbpA interact with chitin in vitro, whereas in vivo complementation studies reveal that domain 1 is also crucial for mucin binding and intestinal colonization. Bacterial binding studies show that domains 2 and 3 bind to the V. cholerae surface. Finally, mouse virulence assays show that only the first three domains of GbpA are required for colonization. These results explain how GbpA provides structural/functional modular interactions between V. cholerae, intestinal epithelium and chitinous exoskeletons.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Molecular Microbiology, College of Life Sciences, University of Dundee, Dundee, United Kingdom.