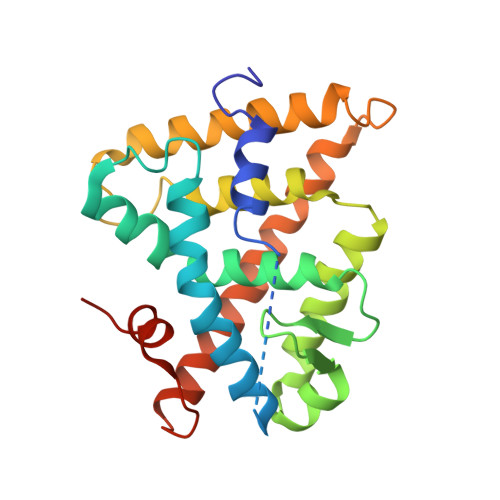
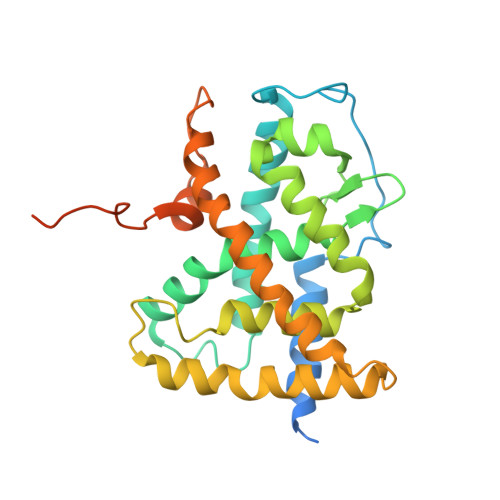
CHARACTERIZATION OF THE INTERACTION BETWEEN RAR/RXR HETERODIMERS AND TRANSCRIPTIONAL COACTIVATORS THROUGH STRUCTURAL AND FLUORESCENCE ANISOTROPY STUDIES
Pogenberg, V., Guichou, J.F., Vivat-Hannah, V., Kammerer, S., Perez, E., Germain, P., De Lera, A.R., Gronemeyer, H., Royer, C.A., Bourguet, W.(2005) J Biol Chem 280: 1625-1633
- PubMed: 15528208
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M409302200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1XDK - PubMed Abstract:
Retinoid receptors (RARs and RXRs) are ligand-activated transcription factors that regulate the transcription of target genes by recruiting coregulator complexes at cognate promoters. To understand the effects of heterodimerization and ligand binding on coactivator recruitment, we solved the crystal structure of the complex between the RARbeta/RXRalpha ligand-binding domain heterodimer, its 9-cis retinoic acid ligand, and an LXXLL-containing peptide (termed NR box 2) derived from the nuclear receptor interaction domain (NID) of the TRAP220 coactivator. In parallel, we measured the binding affinities of the isolated NR box 2 peptide or the full-length NID of the coactivator SRC-1 for retinoid receptors in the presence of various types of ligands. Our correlative analysis of three-dimensional structures and fluorescence data reveals that heterodimerization does not significantly alter the structure of individual subunits or their intrinsic capacity to interact with NR box 2. Similarly, we show that the ability of a protomer to recruit NR box 2 does not vary as a function of the ligand binding status of the partner receptor. In contrast, the strength of the overall association between the heterodimer and the full-length SRC-1 NID is dictated by the combinatorial action of RAR and RXR ligands, the simultaneous presence of the two receptor agonists being required for highest binding affinity. We identified an LXXLL peptide-driven mechanism by which the concerted reorientation of three phenylalanine side chains generates an "aromatic clamp" that locks the RXR activation helix H12 in the transcriptionally active conformation. Finally, we show how variations of helix H11-ligand interactions can alter the communication pathway linking helices H11, H12, and the connecting loop L11-12 to the coactivator-binding site. Together, our results reveal molecular and structural features that impact on the ligand-dependent interaction of the RAR/RXR heterodimer with nuclear receptor coactivators.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre de Biochimie Structurale, CNRS U5048-INSERM U554-UM1, Faculté de Pharmacie, 15 avenue Charles Flahault, 34093 Montpellier, France.