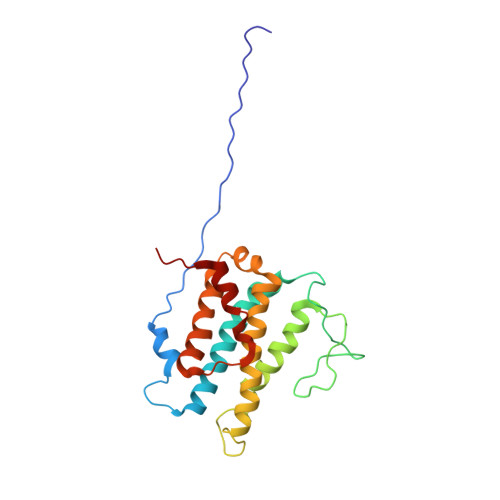
NMR solution structure of Mob1, a mitotic exit network protein and its interaction with an NDR kinase peptide
Ponchon, L., Dumas, C., Kajava, A.V., Fesquet, D., Padilla, A.(2004) J Mol Biol 337: 167-182
- PubMed: 15001360
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.01.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1R3B - PubMed Abstract:
Proteins of the Mob1/phocein family are found in all eukaryotic cells. In yeast, they are activating subunits of Dbf2-related protein kinases involved in cell cycle control. Despite the wide occurrence of these proteins, their biological functions remain poorly understood. Here we report the solution structure of the Mob1 protein from Xenopus laevis solved by heteronuclear multidimensional NMR. The structure reveals a fold constituted by a central left-handed four-helix bundle, one connecting helix, two flanking helices and a long flexible loop. The clustering of two Cys and two His residues, and zinc measurement by atomic absorption spectroscopy support the existence of a zinc ion binding site. Our NMR structure is in good agreement with the recently described X-ray structure of human Mob1-A. Chemical shift perturbations observed upon addition of a peptide encompassing the basic region of the N-terminal regulatory domain of NDR kinase were used to identify and map a specific interaction between Mob1 and this kinase. The chemical shift changes indicate that the main interaction occurs on the acidic and conserved surface of Mob1. This surface was previously hypothesized to be the interaction surface according to the X-ray structure and was identified as functionally important in yeast. Our data suggest that the NDR kinase is a functional Dbf2 homologue in animal cells and contributes to the understanding of the molecular function of Mob1 proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre de Biochimie Structurale (INSERM U554-CNRS UMR5048-UM1), 29 rue de Navacelles, 34090 Montpellier, France.