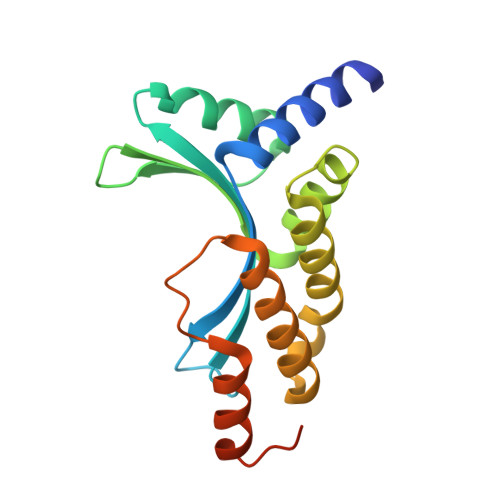
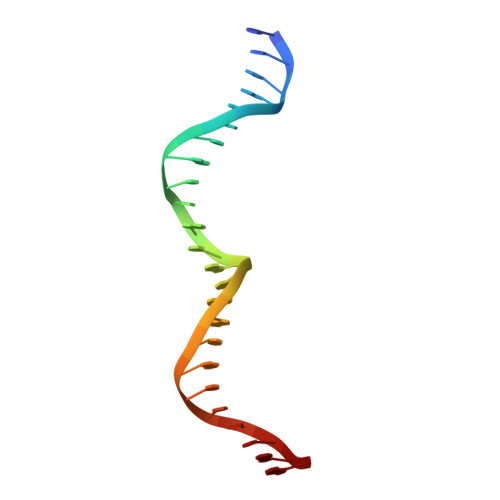
Crystal Structure of the Homing Endonuclease I-Cvui Provides a New Template for Genome Modification
Molina, R., Redondo, P., Lopez-Mendez, B., Villate, M., Merino, N., Blanco, F.J., Valton, J., Grizot, S., Duchateau, P., Prieto, J., Montoya, G.(2015) J Biol Chem 290: 28727
- PubMed: 26363068
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.678342
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5A72, 5A74, 5A77, 5A78 - PubMed Abstract:
Homing endonucleases recognize and generate a DNA double-strand break, which has been used to promote gene targeting. These enzymes recognize long DNA stretches; they are highly sequence-specific enzymes and display a very low frequency of cleavage even in complete genomes. Although a large number of homing endonucleases have been identified, the landscape of possible target sequences is still very limited to cover the complexity of the whole eukaryotic genome. Therefore, the finding and molecular analysis of homing endonucleases identified but not yet characterized may widen the landscape of possible target sequences. The previous characterization of protein-DNA interaction before the engineering of new homing endonucleases is essential for further enzyme modification. Here we report the crystal structure of I-CvuI in complex with its target DNA and with the target DNA of I-CreI, a homologue enzyme widely used in genome engineering. To characterize the enzyme cleavage mechanism, we have solved the I-CvuI DNA structures in the presence of non-catalytic (Ca(2+)) and catalytic ions (Mg(2+)). We have also analyzed the metal dependence of DNA cleavage using Mg(2+) ions at different concentrations ranging from non-cleavable to cleavable concentrations obtained from in vitro cleavage experiments. The structure of I-CvuI homing endonuclease expands the current repertoire for engineering custom specificities, both by itself as a new scaffold alone and in hybrid constructs with other related homing endonucleases or other DNA-binding protein templates.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Structural Biology and Biocomputing Programme, Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), Macromolecular Crystallography Group, C/Melchor Fernández Almagro 3, 28029 Madrid, Spain.