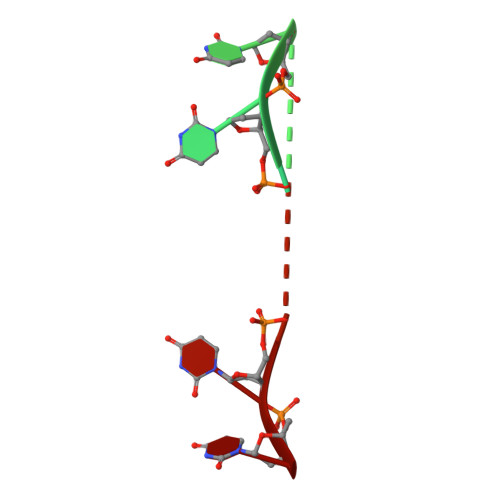
Unraveling the mechanism of recognition of the 3' splice site of the adenovirus major late promoter intron by the alternative splicing factor PUF60.
Hsiao, H.T., Crichlow, G.V., Murphy, J.W., Folta-Stogniew, E.J., Lolis, E.J., Braddock, D.T.(2020) PLoS One 15: e0242725-e0242725
- PubMed: 33253191
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0242725
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5KVY, 5KW1, 5KW6, 5KWQ - PubMed Abstract:
Pre-mRNA splicing is critical for achieving required amounts of a transcript at a given time and for regulating production of encoded protein. A given pre-mRNA may be spliced in many ways, or not at all, giving rise to multiple gene products. Numerous splicing factors are recruited to pre-mRNA splice sites to ensure proper splicing. One such factor, the 60 kDa poly(U)-binding splicing factor (PUF60), is recruited to sites that are not always spliced, but rather function as alternative splice sites. In this study, we characterized the interaction of PUF60 with a splice site from the adenovirus major late promoter (the AdML 3' splice site, AdML3'). We found that the PUF60-AdML3' dissociation constants are in the micromolar range, with the binding affinity predominantly provided by PUF60's two central RNA recognition motifs (RRMs). A 1.95 Å crystal structure of the two PUF60 RRMs in complex with AdML3' revealed a dimeric organization placing two stretches of nucleic acid tracts in opposing directionalities, which can cause looping of nucleic acid and explain how PUF60 affects pre-mRNA geometry to effect splicing. Solution characterization of this complex by light-scattering and UV/Vis spectroscopy suggested a potential 2:1 (PUF602:AdML3') stoichiometry, consistent with the crystal structure. This work defines the sequence specificity of the alternative splicing factor PUF60 at the pre-mRNA 3' splice site. Our observations suggest that control of pre-mRNA directionality is important in the early stage of spliceosome assembly, and advance our understanding of the molecular mechanism by which alternative and constitutive splicing factors differentiate among 3' splice sites.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pathology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, United States of America.