The structural basis of RNA-catalyzed RNA polymerization.
Shechner, D.M., Bartel, D.P.(2011) Nat Struct Mol Biol 18: 1036-1042
- PubMed: 21857665
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2107
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3R1H, 3R1L - PubMed Abstract:
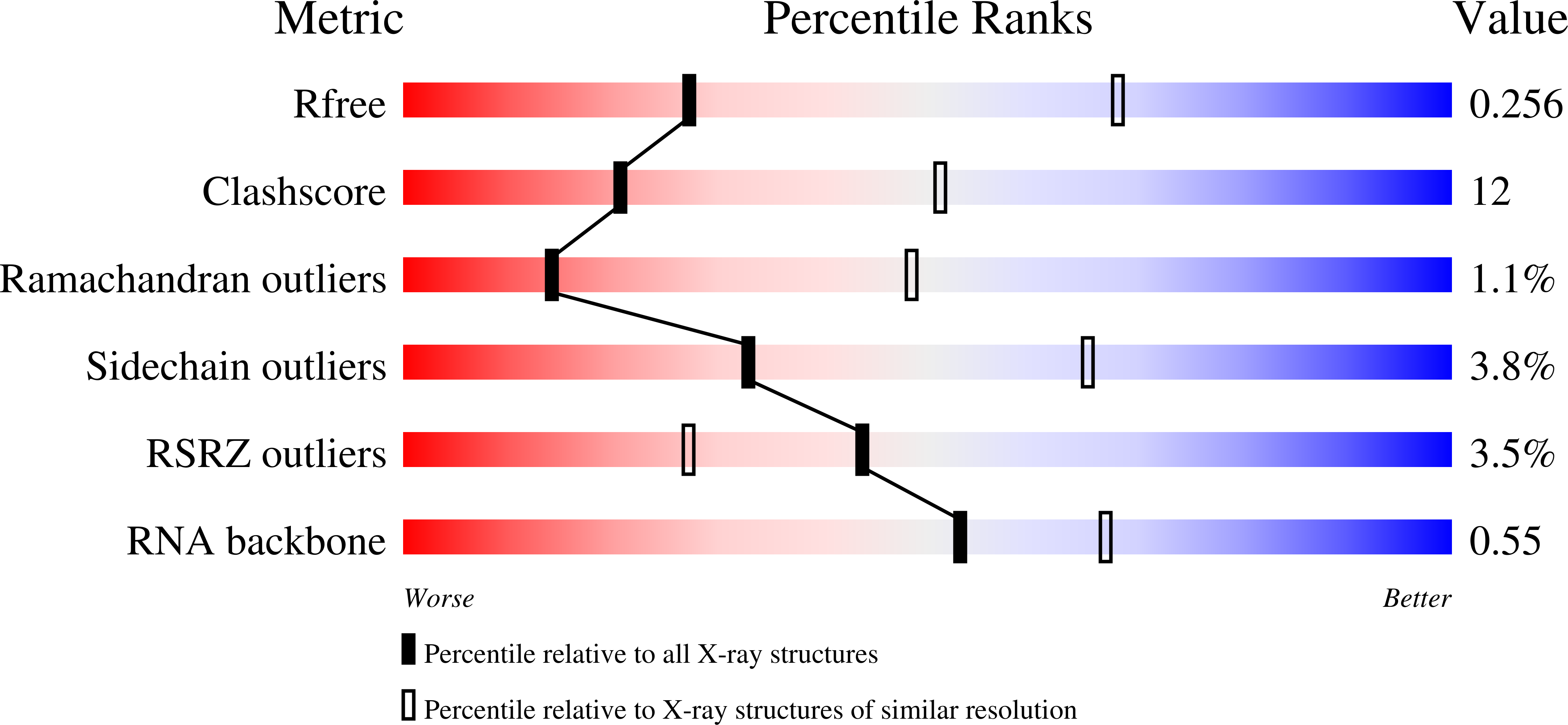
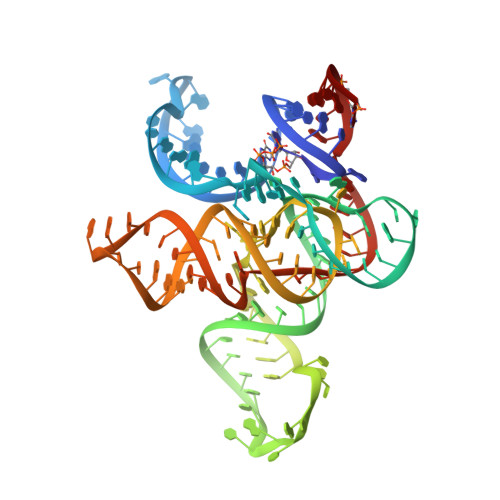
Early life presumably required polymerase ribozymes capable of replicating RNA. Known polymerase ribozymes best approximating such replicases use as their catalytic engine an RNA-ligase ribozyme originally selected from random RNA sequences. Here we report 3.15-Å crystal structures of this ligase trapped in catalytically viable preligation states, with the 3'-hydroxyl nucleophile positioned for in-line attack on the 5'-triphosphate. Guided by metal- and solvent-mediated interactions, the 5'-triphosphate hooks into the major groove of the adjoining RNA duplex in an unanticipated conformation. Two phosphates and the nucleophile jointly coordinate an active-site metal ion. Atomic mutagenesis experiments demonstrate that active-site nucleobase and hydroxyl groups also participate directly in catalysis, collectively playing a role that in proteinaceous polymerases is performed by a second metal ion. Thus artificial ribozymes can use complex catalytic strategies that differ markedly from those of analogous biological enzymes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA.