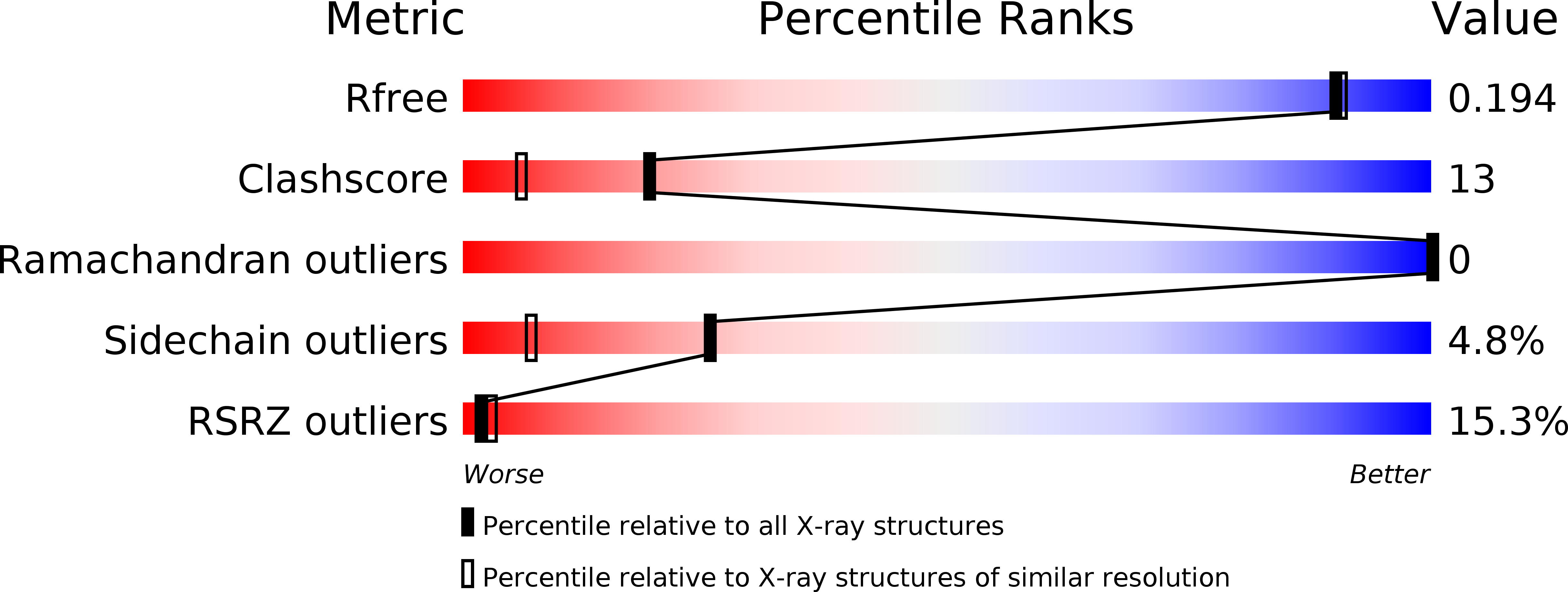
Molecular basis for branched steviol glucoside biosynthesis.
Lee, S.G., Salomon, E., Yu, O., Jez, J.M.(2019) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116: 13131-13136
- PubMed: 31182573
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1902104116
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6O86, 6O87, 6O88 - PubMed Abstract:
Steviol glucosides, such as stevioside and rebaudioside A, are natural products roughly 200-fold sweeter than sugar and are used as natural, noncaloric sweeteners. Biosynthesis of rebaudioside A, and other related stevia glucosides, involves formation of the steviol diterpenoid followed by a series of glycosylations catalyzed by uridine diphosphate (UDP)-dependent glucosyltransferases. UGT76G1 from Stevia rebaudiana catalyzes the formation of the branched-chain glucoside that defines the stevia molecule and is critical for its high-intensity sweetness. Here, we report the 3D structure of the UDP-glucosyltransferase UGT76G1, including a complex of the protein with UDP and rebaudioside A bound in the active site. The X-ray crystal structure and biochemical analysis of site-directed mutants identifies a catalytic histidine and how the acceptor site of UGT76G1 achieves regioselectivity for branched-glucoside synthesis. The active site accommodates a two-glucosyl side chain and provides a site for addition of a third sugar molecule to the C3' position of the first C13 sugar group of stevioside. This structure provides insight on the glycosylation of other naturally occurring sweeteners, such as the mogrosides from monk fruit, and a possible template for engineering of steviol biosynthesis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biology, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO 63130.