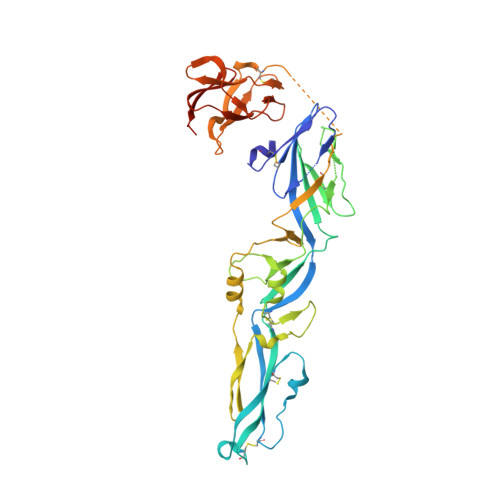
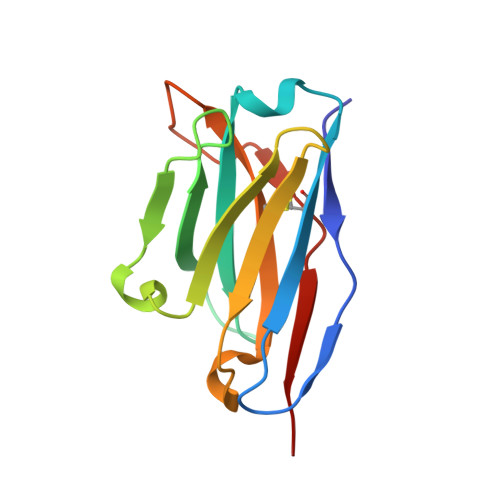
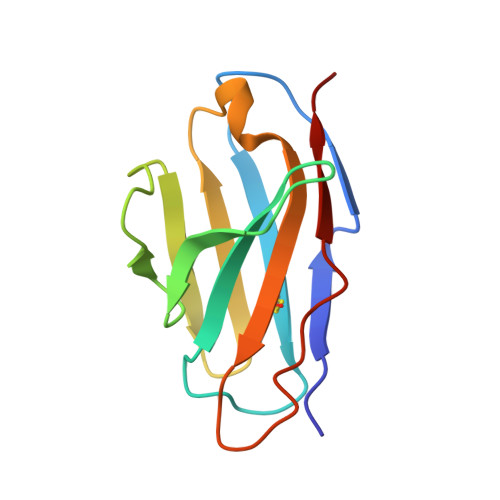
Molecular Basis of a Protective/Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody Targeting Envelope Proteins of both Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus and Louping Ill Virus.
Yang, X., Qi, J., Peng, R., Dai, L., Gould, E.A., Gao, G.F., Tien, P.(2019) J Virol 93
- PubMed: 30760569
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02132-18
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6J5C, 6J5D, 6J5F, 6J5G - PubMed Abstract:
Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) and louping ill virus (LIV) are members of the tick-borne flaviviruses (TBFVs) in the family Flaviviridae which cause encephalomeningitis and encephalitis in humans and other animals. Although vaccines against TBEV and LIV are available, infection rates are rising due to the low vaccination coverage. To date, no specific therapeutics have been licensed. Several neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) show promising effectiveness in the control of TBFVs, but the underlying molecular mechanisms are yet to be characterized. Here, we determined the crystal structures of the LIV envelope (E) protein and report the comparative structural analysis of a TBFV broadly neutralizing murine MAb (MAb 4.2) in complex with either the LIV or TBEV E protein. The structures reveal that MAb 4.2 binds to the lateral ridge of domain III of the E protein (EDIII) of LIV or TBEV, an epitope also reported for other potently neutralizing MAbs against mosquito-borne flaviviruses (MBFVs), but adopts a unique binding orientation. Further structural analysis suggested that MAb 4.2 may neutralize flavivirus infection by preventing the structural rearrangement required for membrane fusion during virus entry. These findings extend our understanding of the vulnerability of TBFVs and other flaviviruses (including MBFVs) and provide an avenue for antibody-based TBFV antiviral development. IMPORTANCE Understanding the mechanism of antibody neutralization/protection against a virus is crucial for antiviral countermeasure development. Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) and louping ill virus (LIV) are tick-borne flaviviruses (TBFVs) in the family Flaviviridae They cause encephalomeningitis and encephalitis in humans and other animals. Although vaccines for both viruses are available, infection rates are rising due to low vaccination coverage. In this study, we solved the crystal structures of the LIV envelope protein (E) and a broadly neutralizing/protective TBFV MAb, MAb 4.2, in complex with E from either TBEV or LIV. Key structural features shared by TBFV E proteins were analyzed. The structures of E-antibody complexes showed that MAb 4.2 targets the lateral ridge of both the TBEV and LIV E proteins, a vulnerable site in flaviviruses for other potent neutralizing MAbs. Thus, this site represents a promising target for TBFV antiviral development. Further, these structures provide important information for understanding TBFV antigenicity.
Organizational Affiliation:
CAS Key Laboratory of Pathogenic Microbiology and Immunology, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Beijing, China.