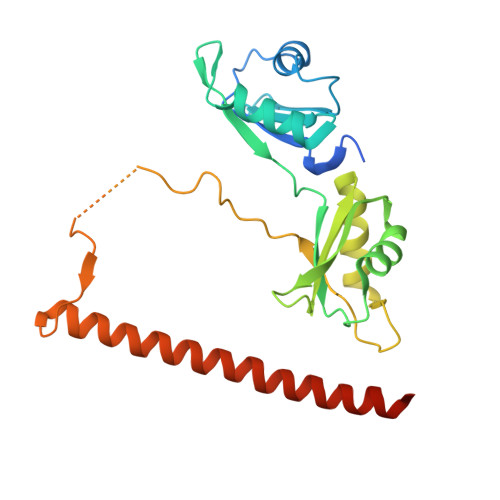
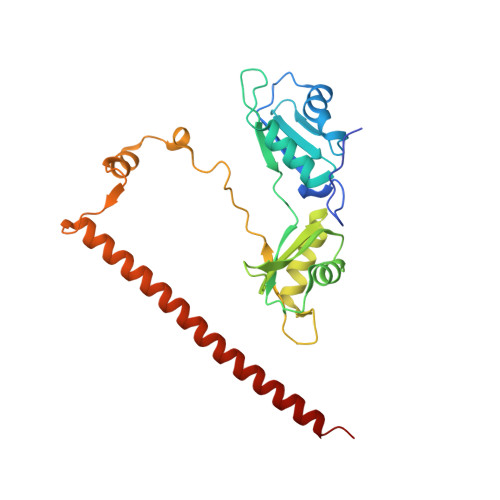
Crystal structure of a SFPQ/PSPC1 heterodimer provides insights into preferential heterodimerization of human DBHS family proteins.
Huang, J., Casas Garcia, G.P., Perugini, M.A., Fox, A.H., Bond, C.S., Lee, M.(2018) J Biol Chem 293: 6593-6602
- PubMed: 29530979
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA117.001451
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5WPA - PubMed Abstract:
Members of the Drosophila behavior human splicing (DBHS) protein family are nuclear proteins implicated in many layers of nuclear functions, including RNA biogenesis as well as DNA repair. Definitive of the DBHS protein family, the conserved DBHS domain provides a dimerization platform that is critical for the structural integrity and function of these proteins. The three human DBHS proteins, splicing factor proline- and glutamine-rich (SFPQ), paraspeckle component 1 (PSPC1), and non-POU domain-containing octamer-binding protein (NONO), form either homo- or heterodimers; however, the relative affinity and mechanistic details of preferential heterodimerization are yet to be deciphered. Here we report the crystal structure of a SFPQ/PSPC1 heterodimer to 2.3-Å resolution and analyzed the subtle structural differences between the SFPQ/PSPC1 heterodimer and the previously characterized SFPQ homodimer. Analytical ultracentrifugation to estimate the dimerization equilibrium of the SFPQ-containing dimers revealed that the SFPQ-containing dimers dissociate at low micromolar concentrations and that the heterodimers have higher affinities than the homodimer. Moreover, we observed that the apparent dissociation constant for the SFPQ/PSPC1 heterodimer was over 6-fold lower than that of the SFPQ/NONO heterodimer. We propose that these differences in dimerization affinity may represent a potential mechanism by which PSPC1 at a lower relative cellular abundance can outcompete NONO to heterodimerize with SFPQ.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Department of Biochemistry and Genetics, La Trobe Institute for Molecular Science, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Victoria 3086 and.