Identification and mechanism of ABA receptor antagonism.
Melcher, K., Xu, Y., Ng, L.M., Zhou, X.E., Soon, F.F., Chinnusamy, V., Suino-Powell, K.M., Kovach, A., Tham, F.S., Cutler, S.R., Li, J., Yong, E.L., Zhu, J.K., Xu, H.E.(2010) Nat Struct Mol Biol 17: 1102-1108
- PubMed: 20729862
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1887
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
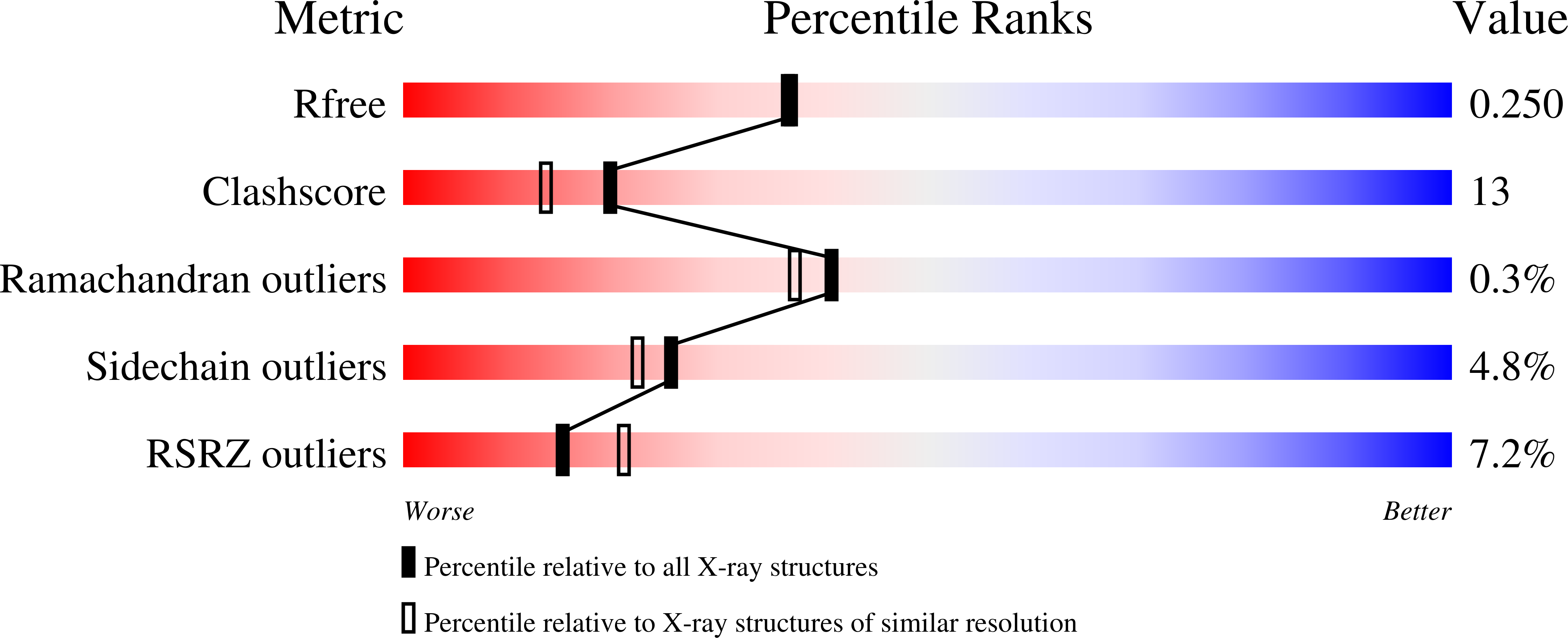
3NMH, 3NMN, 3NMP, 3NMT, 3NMV - PubMed Abstract:
The phytohormone abscisic acid (ABA) functions through a family of fourteen PYR/PYL receptors, which were identified by resistance to pyrabactin, a synthetic inhibitor of seed germination. ABA activates these receptors to inhibit type 2C protein phosphatases, such as ABI1, yet it remains unclear whether these receptors can be antagonized. Here we demonstrate that pyrabactin is an agonist of PYR1 and PYL1 but is unexpectedly an antagonist of PYL2. Crystal structures of the PYL2-pyrabactin and PYL1-pyrabactin-ABI1 complexes reveal the mechanism responsible for receptor-selective activation and inhibition, which enables us to design mutations that convert PYL1 to a pyrabactin-inhibited receptor and PYL2 to a pyrabactin-activated receptor and to identify new pyrabactin-based ABA receptor agonists. Together, our results establish a new concept of ABA receptor antagonism, illustrate its underlying mechanisms and provide a rational framework for discovering novel ABA receptor ligands.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Structural Sciences, Van Andel Research Institute, Grand Rapids, Michigan, USA. Karsten.Melcher@vai.org