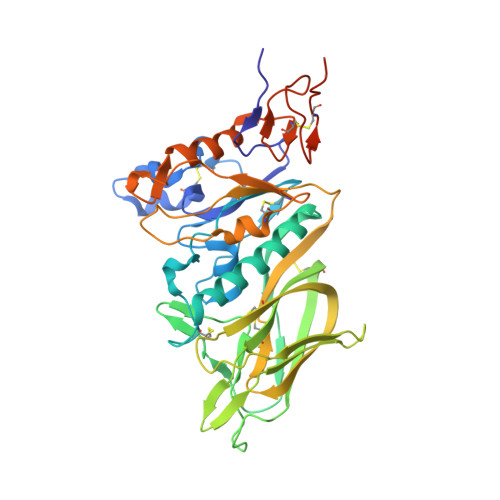
Structure of coronavirus hemagglutinin-esterase offers insight into corona and influenza virus evolution.
Zeng, Q., Langereis, M.A., van Vliet, A.L., Huizinga, E.G., de Groot, R.J.(2008) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105: 9065-9069
- PubMed: 18550812
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0800502105
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3CL4, 3CL5 - PubMed Abstract:
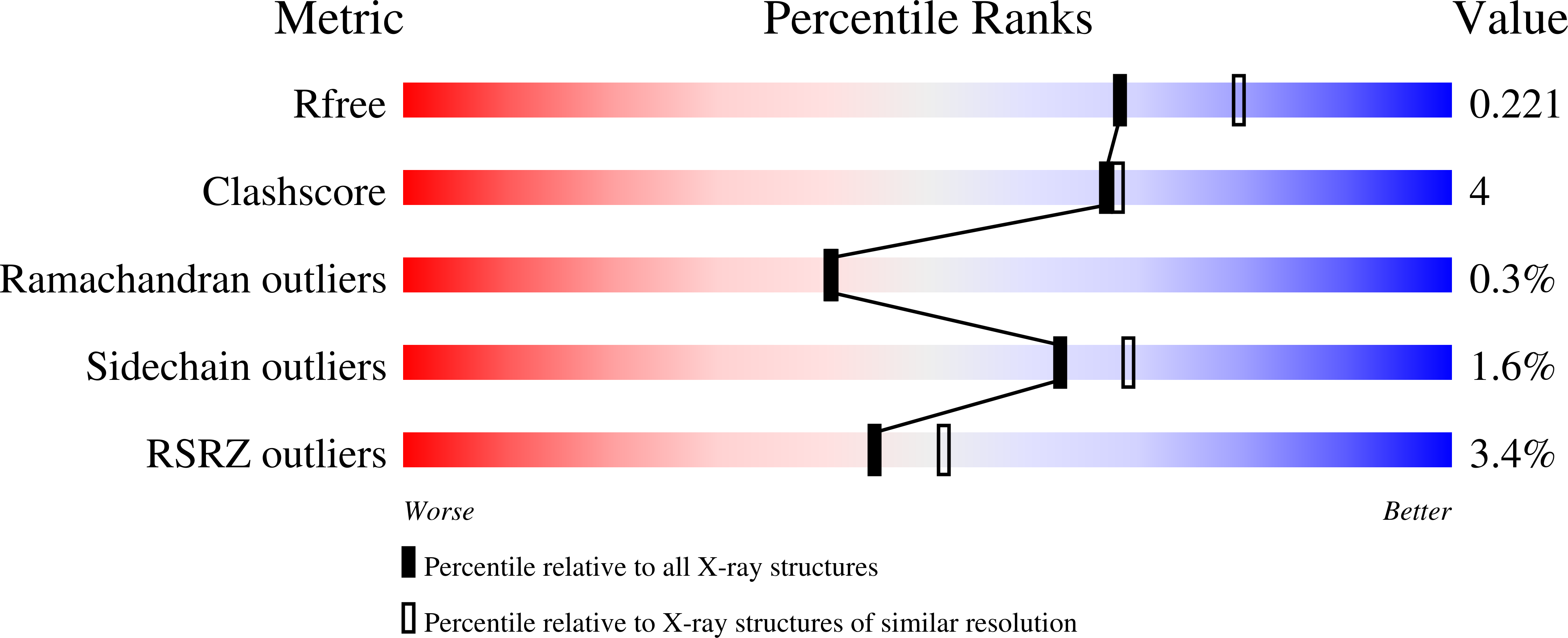
The hemagglutinin-esterases (HEs) are a family of viral envelope glycoproteins that mediate reversible attachment to O-acetylated sialic acids by acting both as lectins and as receptor-destroying enzymes (RDEs). Related HEs occur in influenza C, toro-, and coronaviruses, apparently as a result of relatively recent lateral gene transfer events. Here, we report the crystal structure of a coronavirus (CoV) HE in complex with its receptor. We show that CoV HE arose from an influenza C-like HE fusion protein (HEF). In the process, HE was transformed from a trimer into a dimer, whereas remnants of the fusion domain were adapted to establish novel monomer-monomer contacts. Whereas the structural design of the RDE-acetylesterase domain remained unaltered, the HE receptor-binding domain underwent remodeling to such extent that the ligand is now bound in opposite orientation. This is surprising, because the architecture of the HEF site was preserved in influenza A HA over a much larger evolutionary distance, a switch in receptor specificity and extensive antigenic variation notwithstanding. Apparently, HA and HEF are under more stringent selective constraints than HE, limiting their exploration of alternative binding-site topologies. We attribute the plasticity of the CoV HE receptor-binding site to evolutionary flexibility conferred by functional redundancy between HE and its companion spike protein S. Our findings offer unique insights into the structural and functional consequences of independent protein evolution after interviral gene exchange and open potential avenues to broad-spectrum antiviral drug design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Crystal and Structural Chemistry, Bijvoet Center for Biomolecular Research, Faculty of Sciences, Utrecht University, 3584 CL, Utrecht, The Netherlands.