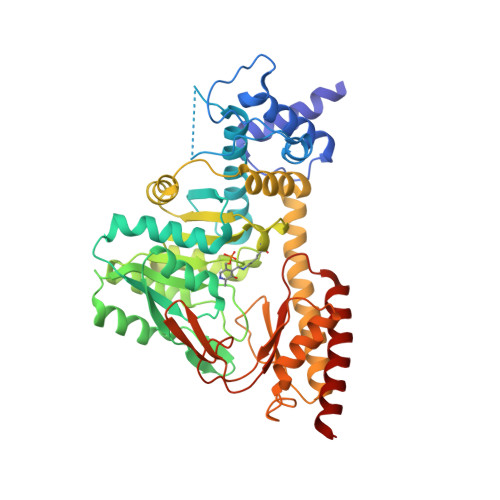
Structure and catalytic mechanism of eukaryotic selenocysteine synthase.
Ganichkin, O.M., Xu, X.M., Carlson, B.A., Mix, H., Hatfield, D.L., Gladyshev, V.N., Wahl, M.C.(2008) J Biol Chem 283: 5849-5865
- PubMed: 18093968
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M709342200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3BC8, 3BCA, 3BCB - PubMed Abstract:
In eukaryotes and Archaea, selenocysteine synthase (SecS) converts O-phospho-L-seryl-tRNA [Ser]Sec into selenocysteyl-tRNA [Ser]Sec using selenophosphate as the selenium donor compound. The molecular mechanisms underlying SecS activity are presently unknown. We have delineated a 450-residue core of mouse SecS, which retained full selenocysteyl-tRNA [Ser]Sec synthesis activity, and determined its crystal structure at 1.65 A resolution. SecS exhibits three domains that place it in the fold type I family of pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent enzymes. Two SecS monomers interact intimately and together build up two identical active sites around PLP in a Schiff-base linkage with lysine 284. Two SecS dimers further associate to form a homotetramer. The N terminus, which mediates tetramer formation, and a large insertion that remodels the active site set SecS aside from other members of the family. The active site insertion contributes to PLP binding and positions a glutamate next to the PLP, where it could repel substrates with a free alpha-carboxyl group, suggesting why SecS does not act on free O-phospho-l-serine. Upon soaking crystals in phosphate buffer, a previously disordered loop within the active site insertion contracted to form a phosphate binding site. Residues that are strictly conserved in SecS orthologs but variant in related enzymes coordinate the phosphate and upon mutation corrupt SecS activity. Modeling suggested that the phosphate loop accommodates the gamma-phosphate moiety of O-phospho-l-seryl-tRNA [Ser]Sec and, after phosphate elimination, binds selenophosphate to initiate attack on the proposed aminoacrylyl-tRNA [Ser]Sec intermediate. Based on these results and on the activity profiles of mechanism-based inhibitors, we offer a detailed reaction mechanism for the enzyme.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max-Planck-Institut für Biophysikalische Chemie, Zelluläre Biochemie/Makromolekulare Röntgenkristallographie, Am Fassberg 11, D-37077 Göttingen, Germany.