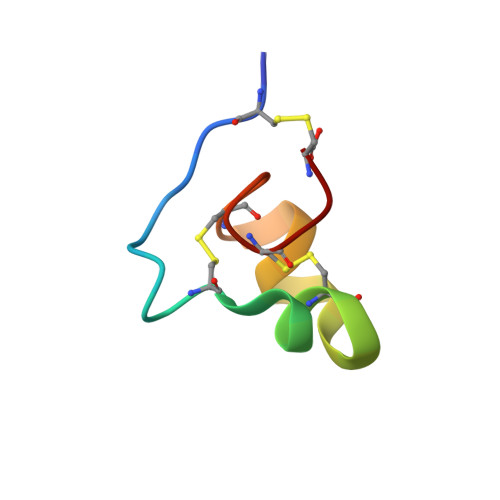
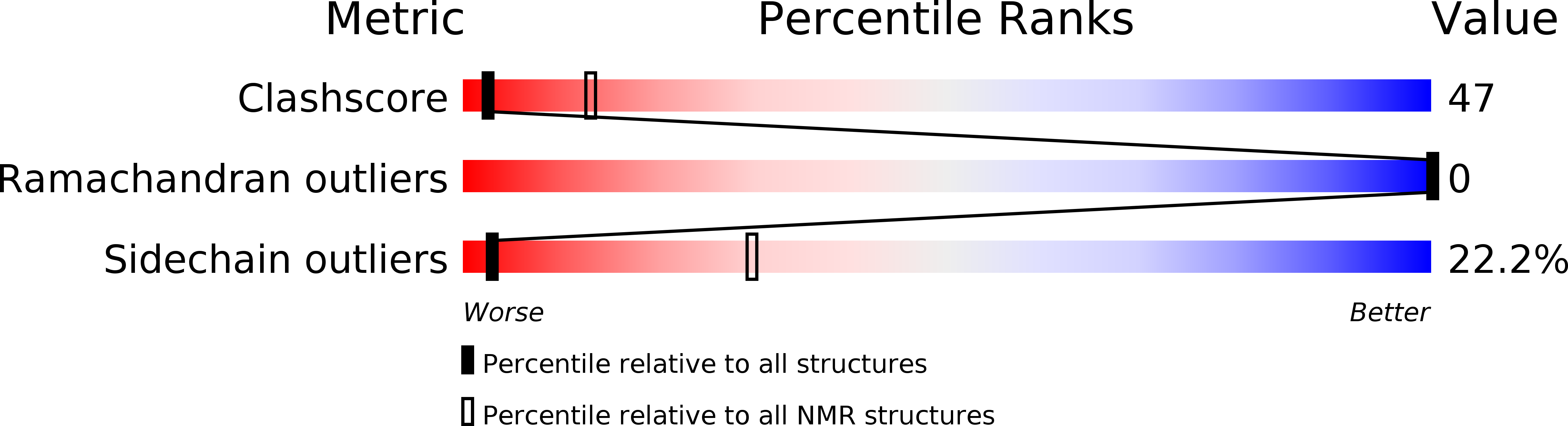Designer and natural peptide toxin blockers of the KcsA potassium channel identified by phage display.
Zhao, R., Dai, H., Mendelman, N., Cuello, L.G., Chill, J.H., Goldstein, S.A.(2015) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112: E7013-E7021
- PubMed: 26627718
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1514728112
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2N6B - PubMed Abstract:
Peptide neurotoxins are powerful tools for research, diagnosis, and treatment of disease. Limiting broader use, most receptors lack an identified toxin that binds with high affinity and specificity. This paper describes isolation of toxins for one such orphan target, KcsA, a potassium channel that has been fundamental to delineating the structural basis for ion channel function. A phage-display strategy is presented whereby ∼1.5 million novel and natural peptides are fabricated on the scaffold present in ShK, a sea anemone type I (SAK1) toxin stabilized by three disulfide bonds. We describe two toxins selected by sorting on purified KcsA, one novel (Hui1, 34 residues) and one natural (HmK, 35 residues). Hui1 is potent, blocking single KcsA channels in planar lipid bilayers half-maximally (Ki) at 1 nM. Hui1 is also specific, inhibiting KcsA-Shaker channels in Xenopus oocytes with a Ki of 0.5 nM whereas Shaker, Kv1.2, and Kv1.3 channels are blocked over 200-fold less well. HmK is potent but promiscuous, blocking KcsA-Shaker, Shaker, Kv1.2, and Kv1.3 channels with Ki of 1-4 nM. As anticipated, one Hui1 blocks the KcsA pore and two conserved toxin residues, Lys21 and Tyr22, are essential for high-affinity binding. Unexpectedly, potassium ions traversing the channel from the inside confer voltage sensitivity to the Hui1 off-rate via Arg23, indicating that Lys21 is not in the pore. The 3D structure of Hui1 reveals a SAK1 fold, rationalizes KcsA inhibition, and validates the scaffold-based approach for isolation of high-affinity toxins for orphan receptors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Brandeis University, Waltham, MA 02453;