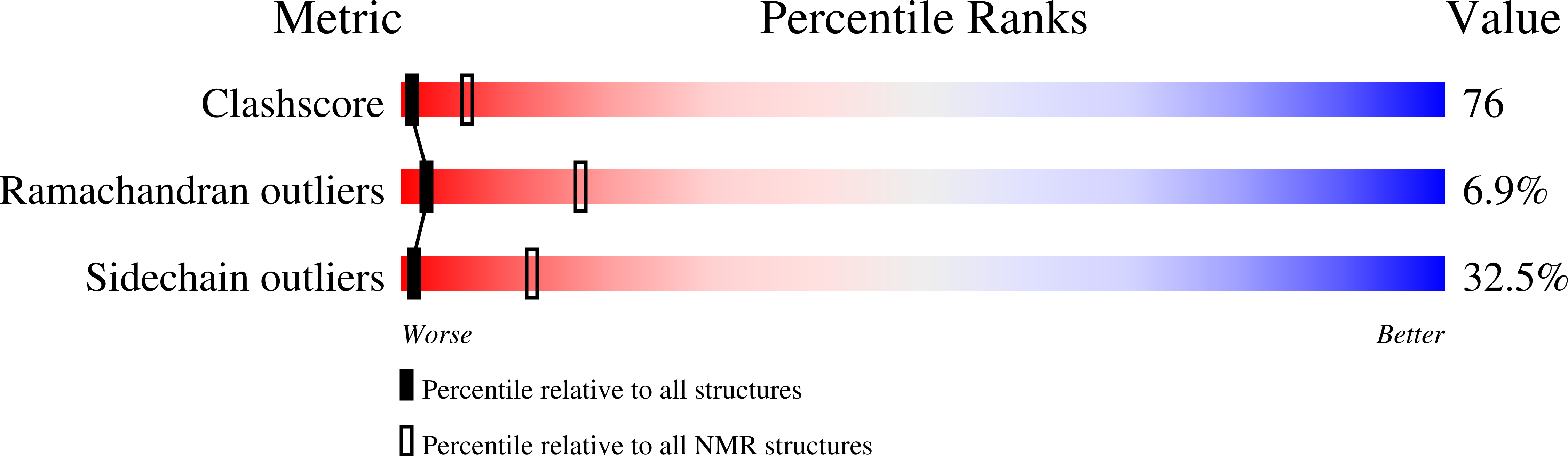The solution structure of the C-terminal modular pair from Clostridium perfringens mu-toxin reveals a noncellulosomal dockerin module
Chitayat, S., Adams, J.J., Furness, H.S., Bayer, E.A., Smith, S.P.(2008) J Mol Biol 381: 1202-1212
- PubMed: 18602403
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.06.050
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2JNK - PubMed Abstract:
The genome of the opportunistic pathogen Clostridium perfringens encodes a large number of secreted glycoside hydrolases. Their predicted activities indicate that they are involved in the breakdown of complex carbohydrates and other glycans found in the mucosal layer of the human gastrointestinal tract, within the extracellular matrix, and on the surface of host cells. One such group of these enzymes is the family 84 glycoside hydrolases, which has predicted hyaluronidase activity and comprises five members [C. perfringens glycoside hydrolase family 84 (CpGH84) A-E]. The first identified member, CpGH84A, corresponds to the mu-toxin whose modular architecture includes an N-terminal catalytic domain, four family 32 carbohydrate-binding modules, three FIVAR modules of unknown function, and a C-terminal putative calcium-binding module. Here, we report the solution NMR structure of the C-terminal modular pair from the mu-toxin. The three-helix bundle FIVAR module displays structural homology to a heparin-binding module within the N-terminal of the a C protein from group B Streptoccocus. The C-terminal module has a typical calcium-binding dockerin fold comprising two anti-parallel helices that form a planar face with EF-hand calcium-binding loops at opposite ends of the module. The size of the helical face of the mu-toxin dockerin module is approximately equal to the planar region recently identified on the surface of a cohesin-like X82 module of CpGH84C. Size-exclusion chromatography and heteronuclear NMR-based chemical shift mapping studies indicate that the helical face of the dockerin module recognizes the CpGH84C X82 module. These studies represent the structural characterization of a noncellulolytic dockerin module and its interaction with a cohesin-like X82 module. Dockerin/X82-mediated enzyme complexes may have important implications in the pathogenic properties of C. perfringens.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada K7L 3N6.