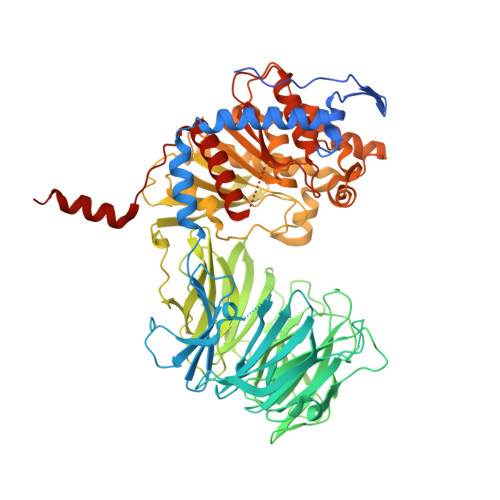
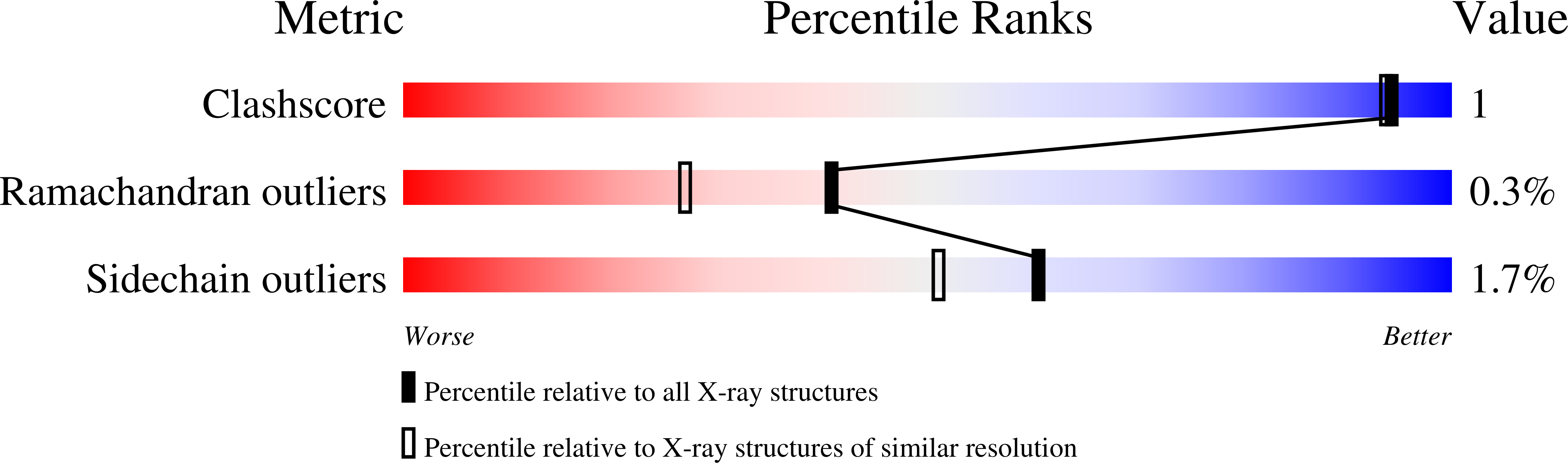Structural and Mechanistic Analysis of Two Prolyl Endopeptidases: Role of Interdomain Dynamics in Catalysis and Specificity
Shan, L., Mathews, I.I., Khosla, C.(2005) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102: 3599-3604
- PubMed: 15738423
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0408286102
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1YR2, 2BKL - PubMed Abstract:
Prolyl endopeptidases (PEPs) are a unique class of serine proteases with considerable therapeutic potential for the treatment of celiac sprue. The crystal structures of two didomain PEPs have been solved in alternative configurations, thereby providing insights into the mode of action of these enzymes. The structure of the Sphingomonas capsulata PEP, solved and refined to 1.8-A resolution, revealed an open configuration of the active site. In contrast, the inhibitor-bound PEP from Myxococcus xanthus was crystallized (1.5-A resolution) in a closed form. Comparative analysis of the two structures highlights a critical role for the domain interface in regulating interdomain dynamics and substrate specificity. Structure-based mutagenesis of the M. xanthus PEP confirms an important role for several interfacial residues. A salt bridge between Arg-572 and Asp-196/Glu-197 appears to act as a latch for opening or closing the didomain enzyme, and Arg-572 and Ile-575 may also help secure the incoming peptide substrate to the open form of the enzyme. Arg-618 and Asp-145 are responsible for anchoring the invariant proline residue in the active site of this postproline-cleaving enzyme. A model is proposed for the docking of a representative substrate PQPQLPYPQPQLP in the active site, where the N-terminal substrate residues interact extensively with the catalytic domain, and the C-terminal residues stretch into the propeller domain. Given the promise of the M. xanthus PEP as an oral therapeutic enzyme for treating celiac sprue, our results provide a strong foundation for further optimization of the PEP's clinically useful features.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA.