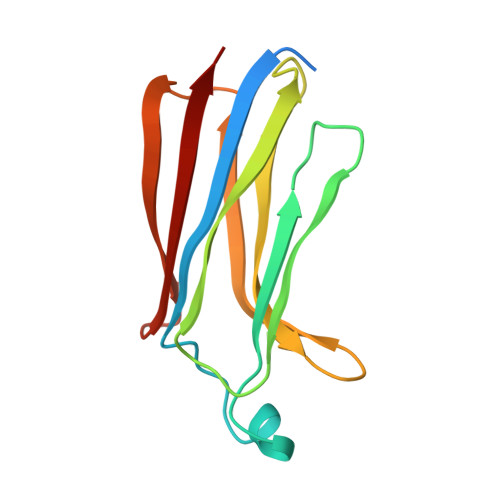
Solution structure and membrane interactions of the C2 domain of cytosolic phospholipase A2.
Xu, G.Y., McDonagh, T., Yu, H.A., Nalefski, E.A., Clark, J.D., Cumming, D.A.(1998) J Mol Biol 280: 485-500
- PubMed: 9665851
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1998.1874
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1BCI - PubMed Abstract:
The amino-terminal, 138 amino acid C2 domain of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2-C2) mediates an initial step in the production of lipid mediators of inflammation: the Ca2+-dependent translocation of the enzyme to intracellular membranes with subsequent liberation of arachidonic acid. The high resolution solution structure of this Ca2+-dependent, lipid-binding domain (CaLB) has been determined using heteronuclear three-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. Secondary structure analysis, derived from several sets of spectroscopic data, shows that the domain is composed of eight antiparallel beta-strands with six interconnecting loops that fits the "type II" topology for C2 domains. Using a total of 2370 distance and torsional restraints, the structure was found to be a beta-sandwich in the "Greek key" motif. The solution structure of cPLA2-C2 domain is very similar to the X-ray crystal structure of the C2 domain of phospholipase-C-delta and phylogenetic analysis clarifies the structural role of highly conserved residues. Calorimetric studies further demonstrate that cPLA2-C2 binds two Ca2+ with observed Kds of approximately 2 microM in an entropically assisted process. Moreover, regions on cPLA2-C2 interacting with membranes were identified by 15N-HSQC-spectroscopy of cPLA2-C2 in the presence of low molecular weight lipid micelles. An extended binding site was identified that binds the phosphocholine headgroup in a Ca2+-dependent manner and also interacts with proximal regions of the membrane surface. Based upon these results, a structural model is presented for the mechanism of association of cPLA2 with its membrane substrate.
Organizational Affiliation:
Small Molecule Drug Discovery, Genetics Institute, 87 Cambridge Park Drive, Cambridge, MA 02140, USA.