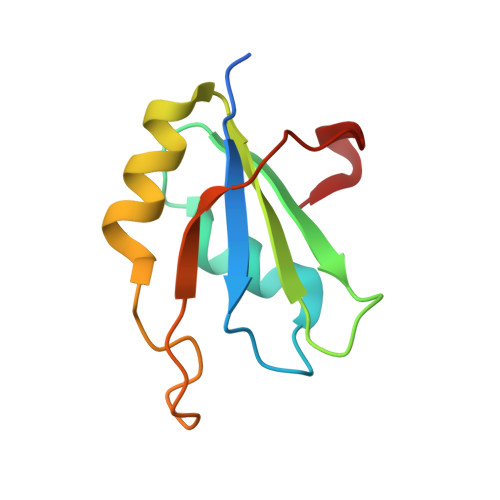
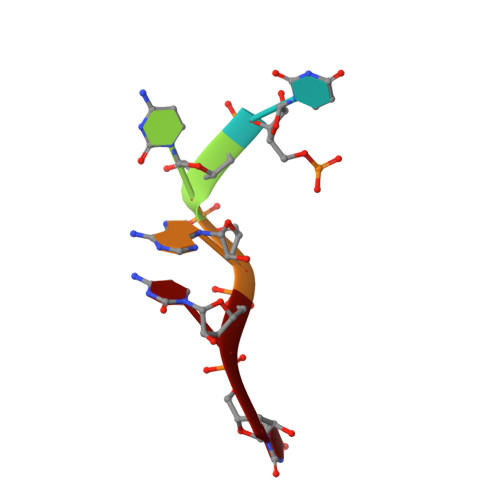
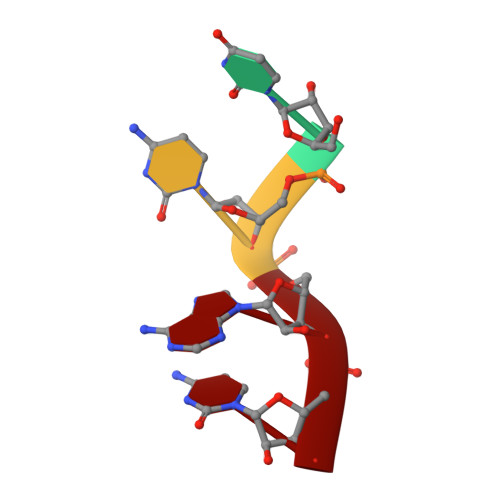
Structural basis underlying CAC RNA recognition by the RRM domain of dimeric RNA-binding protein RBPMS.
Teplova, M., Farazi, T.A., Tuschl, T., Patel, D.J.(2016) Q Rev Biophys 49: e1-e1
- PubMed: 26347403
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033583515000207
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5CYJ, 5DET - PubMed Abstract:
RNA-binding protein with multiple splicing (designated RBPMS) is a higher vertebrate mRNA-binding protein containing a single RNA recognition motif (RRM). RBPMS has been shown to be involved in mRNA transport, localization and stability, with key roles in axon guidance, smooth muscle plasticity, as well as regulation of cancer cell proliferation and migration. We report on structure-function studies of the RRM domain of RBPMS bound to a CAC-containing single-stranded RNA. These results provide insights into potential topologies of complexes formed by the RBPMS RRM domain and the tandem CAC repeat binding sites as detected by photoactivatable-ribonucleoside-enhanced crosslinking and immunoprecipitation. These studies establish that the RRM domain of RBPMS forms a symmetrical dimer in the free state, with each monomer binding sequence-specifically to all three nucleotides of a CAC segment in the RNA bound state. Structure-guided mutations within the dimerization and RNA-binding interfaces of RBPMS RRM on RNA complex formation resulted in both disruption of dimerization and a decrease in RNA-binding affinity as observed by size exclusion chromatography and isothermal titration calorimetry. As anticipated from biochemical binding studies, over-expression of dimerization or RNA-binding mutants of Flag-HA-tagged RBPMS were no longer able to track with stress granules in HEK293 cells, thereby documenting the deleterious effects of such mutations in vivo.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Program,Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center,New York,NY 10065,USA.