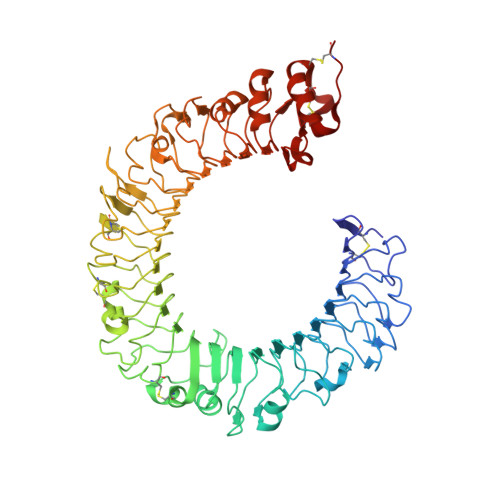
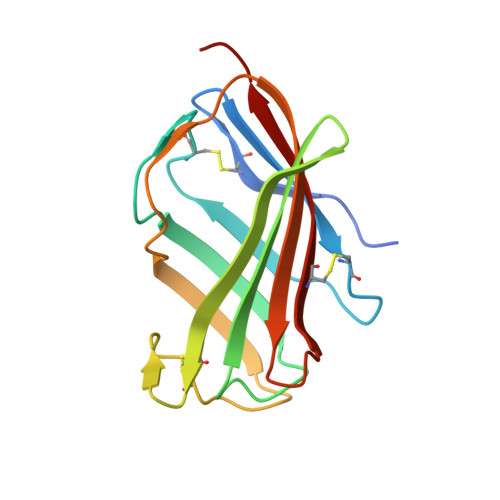
Crystal Structures of Mouse and Human RP105/MD-1 Complexes Reveal Unique Dimer Organization of the Toll-Like Receptor Family.
Ohto, U., Miyake, K., Shimizu, T.(2011) J Mol Biol 413: 815-825
- PubMed: 21959264
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2011.09.020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3B2D, 3T6Q - PubMed Abstract:
The Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4/MD-2 heterodimer senses lipopolysaccharide (LPS). RP105 (radioprotective 105 kDa), a TLR-related molecule, is similar to TLR4 in that the extracellular leucine-rich repeats associate with MD-1, the MD-2-like molecule. MD-2 has a unique hydrophobic cavity that directly binds to lipid A, the active center of LPS. LPS-bound MD-2 opens the secondary interface with TLR4, leading to dimerization of TLR4/MD-2. MD-1 also has a hydrophobic cavity that accommodates lipid IVa, a precursor of lipid A, suggesting a role for the RP105/MD-1 heterodimer in sensing LPS or related microbial products. Little is known, however, about the structure of the RP105/MD-1 heterodimer or its oligomer. Here, we have determined the crystal structures of mouse and human RP105/MD-1 complexes at 1.9 and 2.8 Å resolutions, respectively. Both mouse and human RP105/MD-1 exhibit dimerization of the 1:1 RP105/MD-1 complex, demonstrating a novel organization. The "m"-shaped 2:2 RP105/MD-1 complex exhibits an inverse arrangement, with N-termini interacting in the middle. Thus, the dimerization interface of RP105/MD-1 is located on the opposite side of the complex, compared to the 2:2 TLR4/MD-2 complex. These results demonstrate that the 2:2 RP105/MD-1 complex is distinct from previously reported TLR dimers, including TLR4/MD-2, TLR1/TLR2, TLR2/TLR6, and TLR3, all of which facilitate homotypic or heterotypic interaction of the C-terminal cytoplasmic signaling domain.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Tokyo, Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan.