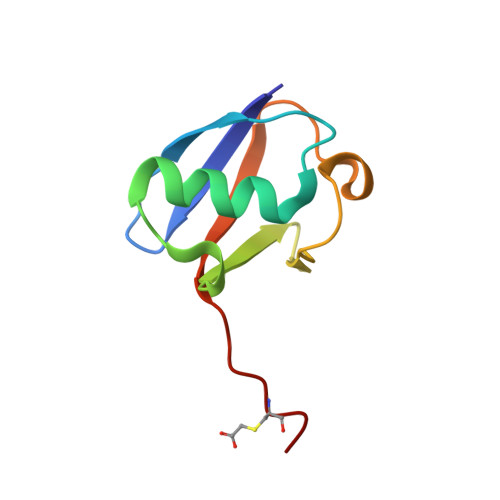
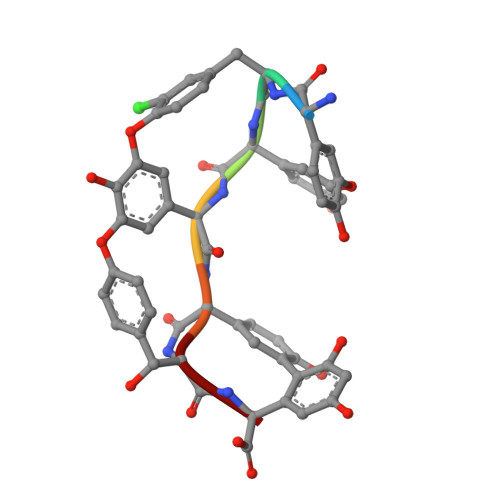
Structure of the complex between teicoplanin and a bacterial cell-wall peptide: use of a carrier-protein approach.
Economou, N.J., Zentner, I.J., Lazo, E., Jakoncic, J., Stojanoff, V., Weeks, S.D., Grasty, K.C., Cocklin, S., Loll, P.J.(2013) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 69: 520-533
- PubMed: 23519660
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444912050469
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3VFJ, 3VFK - PubMed Abstract:
Multidrug-resistant bacterial infections are commonly treated with glycopeptide antibiotics such as teicoplanin. This drug inhibits bacterial cell-wall biosynthesis by binding and sequestering a cell-wall precursor: a D-alanine-containing peptide. A carrier-protein strategy was used to crystallize the complex of teicoplanin and its target peptide by fusing the cell-wall peptide to either MBP or ubiquitin via native chemical ligation and subsequently crystallizing the protein-peptide-antibiotic complex. The 2.05 Å resolution MBP-peptide-teicoplanin structure shows that teicoplanin recognizes its ligand through a combination of five hydrogen bonds and multiple van der Waals interactions. Comparison of this teicoplanin structure with that of unliganded teicoplanin reveals a flexibility in the antibiotic peptide backbone that has significant implications for ligand recognition. Diffraction experiments revealed an X-ray-induced dechlorination of the sixth amino acid of the antibiotic; it is shown that teicoplanin is significantly more radiation-sensitive than other similar antibiotics and that ligand binding increases radiosensitivity. Insights derived from this new teicoplanin structure may contribute to the development of next-generation antibacterials designed to overcome bacterial resistance.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA 19102, USA.