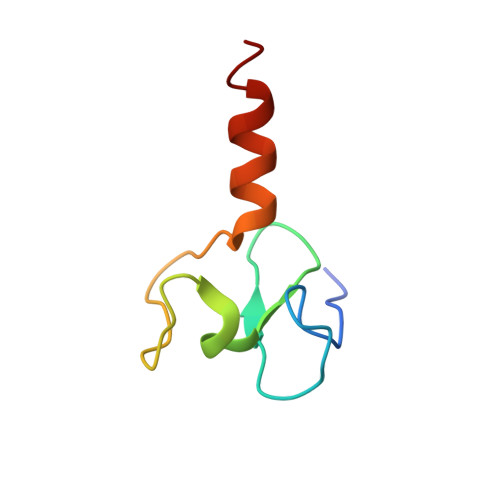
Recognition of unmethylated histone H3 lysine 4 links BHC80 to LSD1-mediated gene repression.
Lan, F., Collins, R.E., De Cegli, R., Alpatov, R., Horton, J.R., Shi, X., Gozani, O., Cheng, X., Shi, Y.(2007) Nature 448: 718-722
- PubMed: 17687328
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06034
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2PUY - PubMed Abstract:
Histone methylation is crucial for regulating chromatin structure, gene transcription and the epigenetic state of the cell. LSD1 is a lysine-specific histone demethylase that represses transcription by demethylating histone H3 on lysine 4 (ref. 1). The LSD1 complex contains a number of proteins, all of which have been assigned roles in events upstream of LSD1-mediated demethylation apart from BHC80 (also known as PHF21A), a plant homeodomain (PHD) finger-containing protein. Here we report that, in contrast to the PHD fingers of the bromodomain PHD finger transcription factor (BPTF) and inhibitor of growth family 2 (ING2), which bind methylated H3K4 (H3K4me3), the PHD finger of BHC80 binds unmethylated H3K4 (H3K4me0), and this interaction is specifically abrogated by methylation of H3K4. The crystal structure of the PHD finger of BHC80 bound to an unmodified H3 peptide has revealed the structural basis of the recognition of H3K4me0. Knockdown of BHC80 by RNA inhibition results in the de-repression of LSD1 target genes, and this repression is restored by the reintroduction of wild-type BHC80 but not by a PHD-finger mutant that cannot bind H3. Chromatin immunoprecipitation showed that BHC80 and LSD1 depend reciprocally on one another to associate with chromatin. These findings couple the function of BHC80 to that of LSD1, and indicate that unmodified H3K4 is part of the 'histone code'. They further raise the possibility that the generation and recognition of the unmodified state on histone tails in general might be just as crucial as post-translational modifications of histone for chromatin and transcriptional regulation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pathology, Harvard Medical School, 77 Ave Louis Pasteur, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.