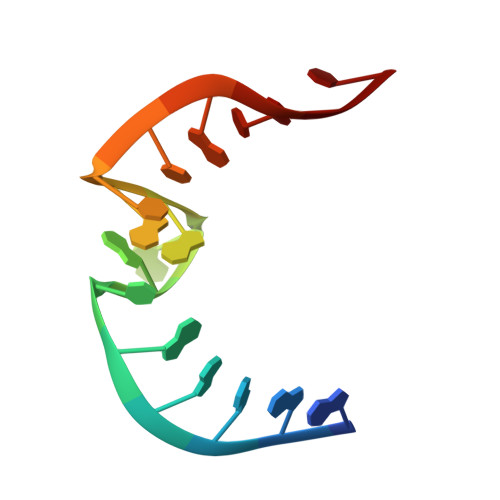
Solution Structure of the Bacillus subtilis T-box Antiterminator RNA: Seven Nucleotide Bulge Characterized by Stacking and Flexibility
Gerdeman, M.S., Henkin, T.M., Hines, J.V.(2003) J Mol Biol 326: 189-201
- PubMed: 12547201
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01339-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1N53 - PubMed Abstract:
The T-box transcription antitermination regulatory system is an important mechanism for regulation of expression of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, amino acid biosynthesis and transporter gene expression in Gram-positive bacteria. Antitermination is dependent on a complex set of interactions between uncharged tRNA and the leader region of the mRNA of the regulated gene. Here, we report the solution structure of a model RNA, based on the Bacillus subtilis tyrS antiterminator, determined to an rmsd of 3.47A for all nine converged structures and 2.66A for the seven structures representing the consensus family. The antiterminator is comprised of two short helices with an intervening 7nt bulge. The bulge region of the antiterminator, which ultimately interacts with the acceptor end of tRNA, exhibits extensive stacking at the 3' end (encompassing the highly conserved ACC residues) and is the site of a pronounced kink between the two flanking helices. The 5' end of the bulge exhibits evidence of conformational flexibility. On the basis of the structural studies, there is no indication that the bases at the 5' end of the bulge that ultimately base-pair with tRNA are pre-organized for binding. Instead, the data are consistent with a model in which the stacking-induced structure at the 3' end of the bulge may facilitate the pre-selection of a set of conformations for the tRNA to sample during binding.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Medicinal Chemistry, College of Pharmacy, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210, USA.