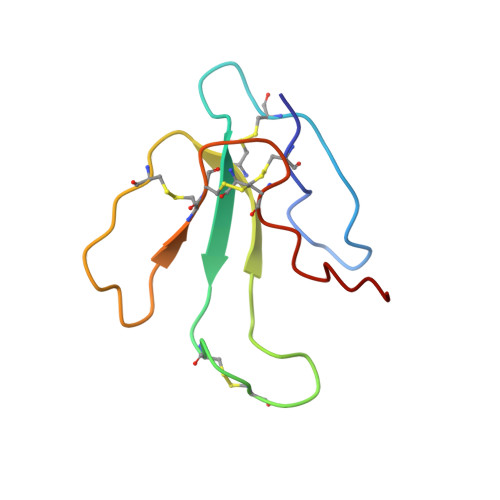
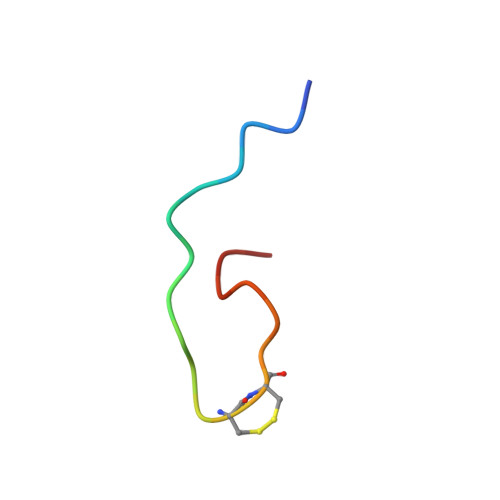
NMR structural analysis of alpha-bungarotoxin and its complex with the principal alpha-neurotoxin-binding sequence on the alpha 7 subunit of a neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.
Moise, L., Piserchio, A., Basus, V.J., Hawrot, E.(2002) J Biol Chem 277: 12406-12417
- PubMed: 11790782
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110320200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1KC4, 1KFH, 1KL8 - PubMed Abstract:
We report a new, higher resolution NMR structure of alpha-bungarotoxin that defines the structure-determining disulfide core and beta-sheet regions. We further report the NMR structure of the stoichiometric complex formed between alpha-bungarotoxin and a recombinantly expressed 19-mer peptide ((178)IPGKRTESFYECCKEPYPD(196)) derived from the alpha7 subunit of the chick neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. A comparison of these two structures reveals binding-induced stabilization of the flexible tip of finger II in alpha-bungarotoxin. The conformational rearrangements in the toxin create an extensive binding surface involving both sides of the alpha7 19-mer hairpin-like structure. At the contact zone, Ala(7), Ser(9), and Ile(11) in finger I and Arg(36), Lys(38), Val(39), and Val(40) in finger II of alpha-bungarotoxin interface with Phe(186), Tyr(187), Glu(188), and Tyr(194) in the alpha7 19-mer underscoring the importance of receptor aromatic residues as critical neurotoxin-binding determinants. Superimposing the structure of the complex onto that of the acetylcholine-binding protein (1I9B), a soluble homologue of the extracellular domain of the alpha7 receptor, places alpha-bungarotoxin at the peripheral surface of the inter-subunit interface occluding the agonist-binding site. The disulfide-rich core of alpha-bungarotoxin is suggested to be tilted in the direction of the membrane surface with finger II extending into the proposed ligand-binding cavity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Pharmacology, Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island 02912, USA.