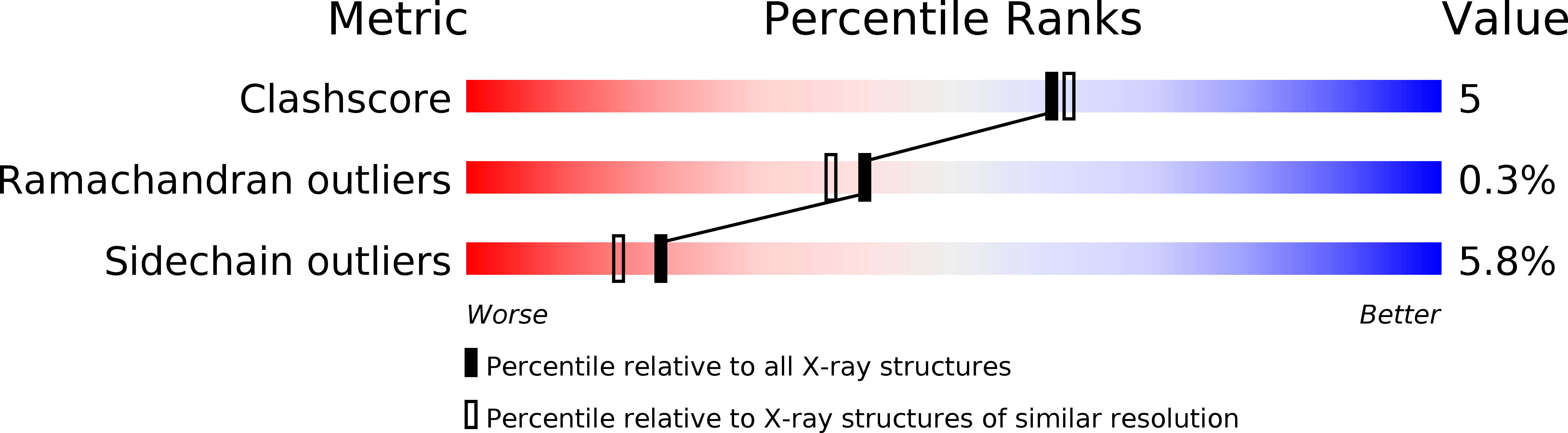pH-dependent structural changes in the active site of p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase point to the importance of proton and water movements during catalysis.
Gatti, D.L., Entsch, B., Ballou, D.P., Ludwig, M.L.(1996) Biochemistry 35: 567-578
- PubMed: 8555229
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi951344i
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IUS, 1IUT, 1IUU, 1IUV, 1IUW, 1IUX - PubMed Abstract:
Deprotonation of p-hydroxybenzoate to the phenolate and reprotonation of the hydroxylated dienone intermediate to form the product are essential steps in the reaction catalyzed by p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase (PHBH). The mechanism by which protons are transferred in these reactions is not obvious, because the substrate bound in the active site is isolated from solvent. Structure analyses of wild-type and mutant PHBH, with bound p-hydroxybenzoate or p-aminobenzoate, reveal a chain of proton donors and acceptors (the hydroxyl groups of Tyr201 and Tyr385, and two water molecules) that can connect the substrate 4-OH to His72, a surface residue. This chain could provide a pathway for proton transfer to and from the substrate. Using various combinations of pH and substrates, we show that in crystalline PHBH ionizable groups in the chain may rotate and change hydrogen-bond orientation. Molecular dynamics simulations have been used to predict the preferred orientation of hydrogen bonds in the chain as a function of the ionization states of substrate and His72. The calculations suggest that changes in the ionization state of the substrate could be associated with changes in orientation of the hydrogen bonds in the chain. Transfer of water between the chain of proton donors and the solvent also appears to be an essential part of the mechanism that provides reversible transfer of protons during the hydroxylation reaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Chemistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor 48109, USA.