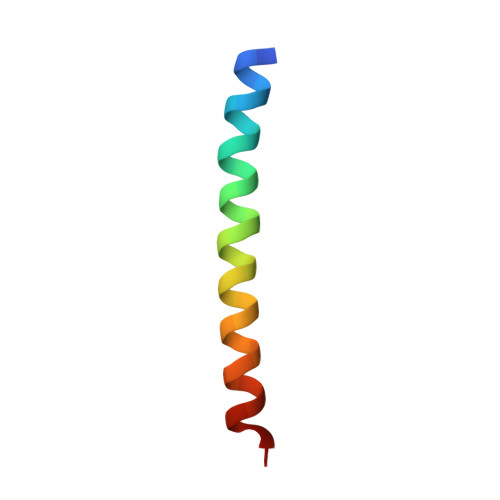
Arc self-association and formation of virus-like capsids are mediated by an N-terminal helical coil motif.
Eriksen, M.S., Nikolaienko, O., Hallin, E.I., Grodem, S., Bustad, H.J., Flydal, M.I., Merski, I., Hosokawa, T., Lascu, D., Akerkar, S., Cuellar, J., Chambers, J.J., O'Connell, R., Muruganandam, G., Loris, R., Touma, C., Kanhema, T., Hayashi, Y., Stratton, M.M., Valpuesta, J.M., Kursula, P., Martinez, A., Bramham, C.R.(2021) FEBS J 288: 2930-2955
- PubMed: 33175445
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.15618
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6YTU - PubMed Abstract:
Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein (Arc) is a protein interaction hub with diverse roles in intracellular neuronal signaling, and important functions in neuronal synaptic plasticity, memory, and postnatal cortical development. Arc has homology to retroviral Gag protein and is capable of self-assembly into virus-like capsids implicated in the intercellular transfer of RNA. However, the molecular basis of Arc self-association and capsid formation is largely unknown. Here, we identified a 28-amino-acid stretch in the mammalian Arc N-terminal (NT) domain that is necessary and sufficient for self-association. Within this region, we identified a 7-residue oligomerization motif, critical for the formation of virus-like capsids. Purified wild-type Arc formed capsids as shown by transmission and cryo-electron microscopy, whereas mutant Arc with disruption of the oligomerization motif formed homogenous dimers. An atomic-resolution crystal structure of the oligomerization region peptide demonstrated an antiparallel coiled-coil interface, strongly supporting NT-NT domain interactions in Arc oligomerization. The NT coil-coil interaction was also validated in live neurons using fluorescence lifetime FRET imaging, and mutation of the oligomerization motif disrupted Arc-facilitated endocytosis. Furthermore, using single-molecule photobleaching, we show that Arc mRNA greatly enhances higher-order oligomerization in a manner dependent on the oligomerization motif. In conclusion, a helical coil in the Arc NT domain supports self-association above the dimer stage, mRNA-induced oligomerization, and formation of virus-like capsids. DATABASE: The coordinates and structure factors for crystallographic analysis of the oligomerization region were deposited at the Protein Data Bank with the entry code 6YTU.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biomedicine, University of Bergen, Norway.