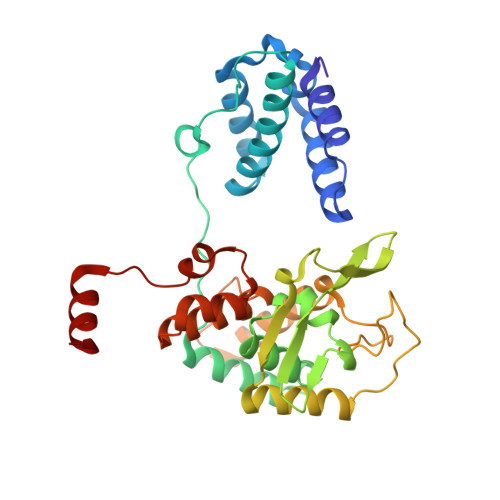
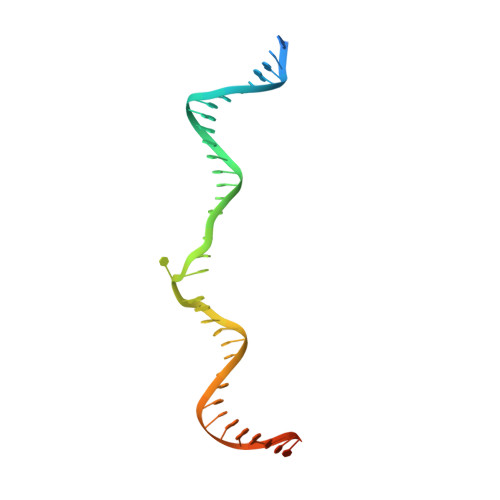
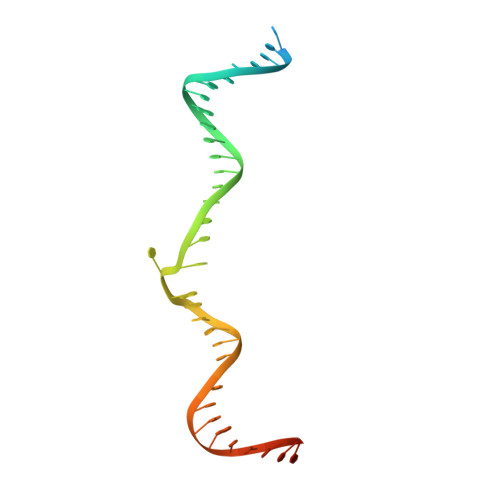
Transposase-DNA Complex Structures Reveal Mechanisms for Conjugative Transposition of Antibiotic Resistance.
Rubio-Cosials, A., Schulz, E.C., Lambertsen, L., Smyshlyaev, G., Rojas-Cordova, C., Forslund, K., Karaca, E., Bebel, A., Bork, P., Barabas, O.(2018) Cell 173: 208-220.e20
- PubMed: 29551265
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.032
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6EMY, 6EMZ, 6EN0, 6EN1, 6EN2 - PubMed Abstract:
Conjugative transposition drives the emergence of multidrug resistance in diverse bacterial pathogens, yet the mechanisms are poorly characterized. The Tn1549 conjugative transposon propagates resistance to the antibiotic vancomycin used for severe drug-resistant infections. Here, we present four high-resolution structures of the conserved Y-transposase of Tn1549 complexed with circular transposon DNA intermediates. The structures reveal individual transposition steps and explain how specific DNA distortion and cleavage mechanisms enable DNA strand exchange with an absolute minimum homology requirement. This appears to uniquely allow Tn916-like conjugative transposons to bypass DNA homology and insert into diverse genomic sites, expanding gene transfer. We further uncover a structural regulatory mechanism that prevents premature cleavage of the transposon DNA before a suitable target DNA is found and generate a peptide antagonist that interferes with the transposase-DNA structure to block transposition. Our results reveal mechanistic principles of conjugative transposition that could help control the spread of antibiotic resistance genes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural and Computational Biology Unit, European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), 69117 Heidelberg, Germany.