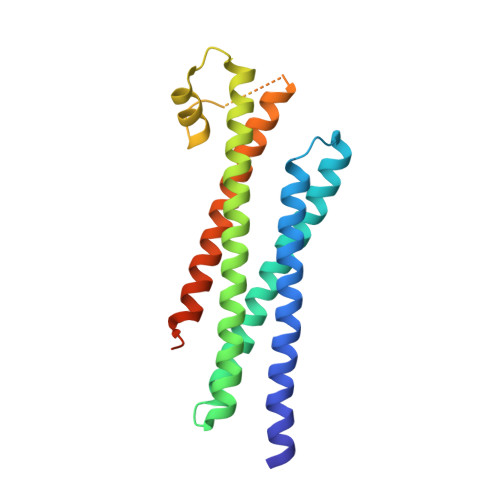
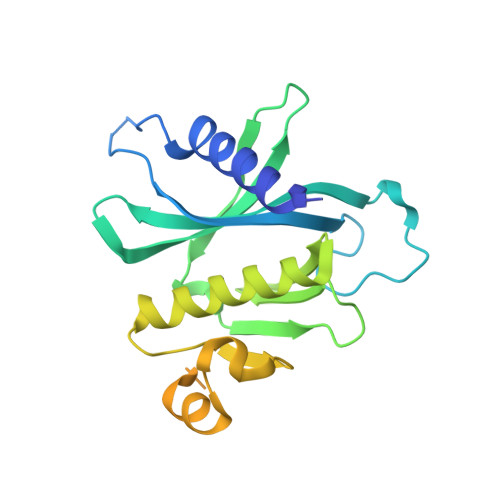
Sec3 promotes the initial binary t-SNARE complex assembly and membrane fusion.
Yue, P., Zhang, Y., Mei, K., Wang, S., Lesigang, J., Zhu, Y., Dong, G., Guo, W.(2017) Nat Commun 8: 14236-14236
- PubMed: 28112172
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14236
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5LG4, 5M4Y - PubMed Abstract:
The soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor-attachment protein receptors (SNAREs) constitute the core machinery for membrane fusion during eukaryotic cell vesicular trafficking. However, how the assembly of the SNARE complex is initiated is unknown. Here we report that Sec3, a component of the exocyst complex that mediates vesicle tethering during exocytosis, directly interacts with the t-SNARE protein Sso2. This interaction promotes the formation of an Sso2-Sec9 'binary' t-SNARE complex, the early rate-limiting step in SNARE complex assembly, and stimulates membrane fusion. The crystal structure of the Sec3-Sso2 complex suggests that Sec3 binding induces conformational changes of Sso2 that are crucial for the relief of its auto-inhibition. Interestingly, specific disruption of the Sec3-Sso2 interaction in cells blocks exocytosis without affecting the function of Sec3 in vesicle tethering. Our study reveals an activation mechanism for SNARE complex assembly, and uncovers a role of the exocyst in promoting membrane fusion in addition to vesicle tethering.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104, USA.