New Structural Insight of C-Terminal Region of Syntenin-1, Enhancing the Molecular Dimerization and Inhibitory Function Related on Syndecan-4 Signaling.
Choi, Y., Yun, J.H., Yoo, J., Kim, H., Lee, I., Son, H.N., Kim, I.S., Yoon, H.S., Zimmermann, P., Couchman, J.R., Cho, H.S., Oh, E.S., Lee, W.(2016) Sci Rep 6: 36818
- PubMed: 27830760
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36818
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5G1D, 5G1E - PubMed Abstract:
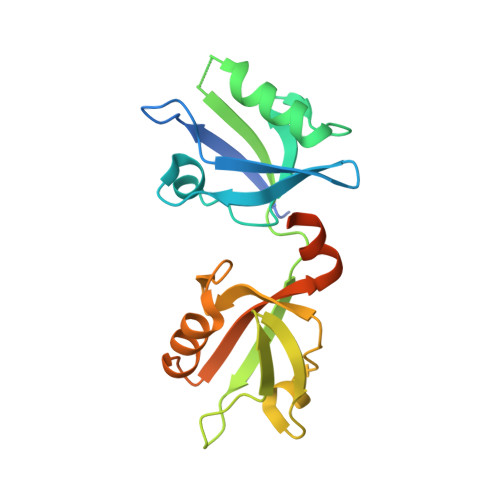
The PDZ domain-containing scaffold protein, syntenin-1, binds to the transmembrane proteoglycan, syndecan-4, but the molecular mechanism/function of this interaction are unknown. Crystal structure analysis of syntenin-1/syndecan-4 cytoplasmic domains revealed that syntenin-1 forms a symmetrical pair of dimers anchored by a syndecan-4 dimer. The syndecan-4 cytoplasmic domain is a compact intertwined dimer with a symmetrical clamp shape and two antiparallel strands forming a cavity within the dimeric twist. The PDZ2 domain of syntenin-1 forms a direct antiparallel interaction with the syndecan-4 cytoplasmic domain, inhibiting the functions of syndecan-4 such as focal adhesion formation. Moreover, C-terminal region of syntenin-1 reveals an essential role for enhancing the molecular homodimerization. Mutation of key syntenin-1 residues involved in the syndecan-4 interaction or homodimer formation abolishes the inhibitory function of syntenin-1, as does deletion of the homodimerization-related syntenin-1 C-terminal domain. Syntenin-1, but not dimer-formation-incompetent mutants, rescued the syndecan-4-mediated inhibition of migration and pulmonary metastasis by B16F10 cells. Therefore, we conclude that syntenin-1 negatively regulates syndecan-4 function via oligomerization and/or syndecan-4 interaction, impacting cytoskeletal organization and cell migration.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Life Sciences, Division of Life and Pharmaceutical Sciences and the Research Center for Cellular Homeostasis, Ewha Womans University, Seoul 120-750, Korea.