Structural Characterisation of the Virulence-Associated Protein Vapg from the Horse Pathogen Rhodococcus Equi.
Okoko, T., Blagova, E.V., Whittingham, J.L., Dover, L.G., Wilkinson, A.J.(2015) Vet Microbiol 179: 42
- PubMed: 25746683
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.01.027
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5AEO - PubMed Abstract:
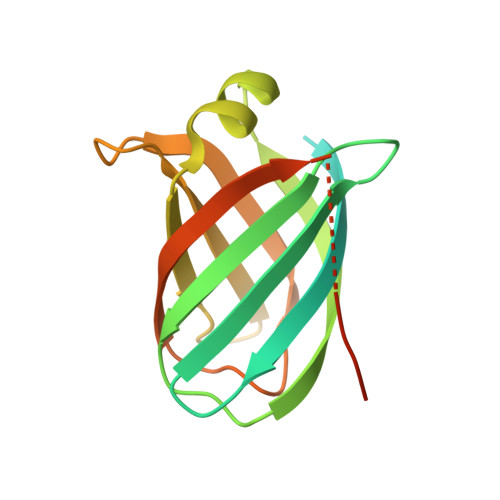
Virulence and host range in Rhodococcus equi depends on the variable pathogenicity island of their virulence plasmids. Notable gene products are a family of small secreted virulence-associated proteins (Vaps) that are critical to intramacrophagic proliferation. Equine-adapted strains, which cause severe pyogranulomatous pneumonia in foals, produce a cell-associated VapA that is necessary for virulence, alongside five other secreted homologues. In the absence of biochemical insight, attention has turned to the structures of these proteins to develop a functional hypothesis. Recent studies have described crystal structures for VapD and a truncate of the VapA orthologue of porcine-adapted strains, VapB. Here, we crystallised the full-length VapG and determined its structure by molecular replacement. Electron density corresponding to the N-terminal domain was not visible suggesting that it is disordered. The protein core adopted a compact elliptical, anti-parallel β-barrel fold with β1-β2-β3-β8-β5-β6-β7-β4 topology decorated by a single peripheral α-helix unique to this family. The high glycine content of the protein allows close packing of secondary structural elements. Topologically, the surface has no indentations that indicate a nexus for molecular interactions. The distribution of polar and apolar groups on the surface of VapG is markedly uneven. One-third of the surface is dominated by exposed apolar side-chains, with no ionisable and only four polar side-chains exposed, giving rise to an expansive flat hydrophobic surface. Other surface regions are more polar, especially on or near the α-helix and a belt around the centre of the β-barrel. Possible functional significance of these recent structures is discussed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Applied Sciences, Faculty of Health and Life Sciences, Northumbria University, Newcastle upon Tyne NE1 8ST, UK.