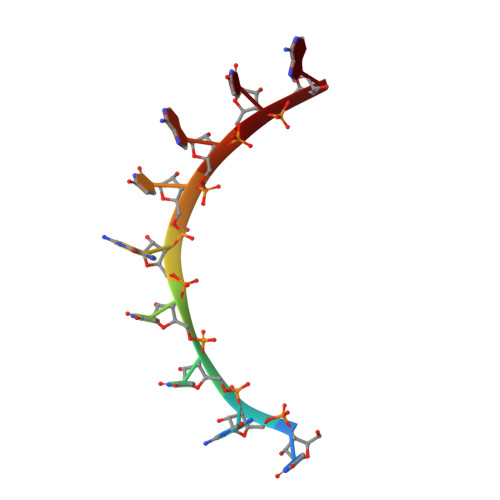
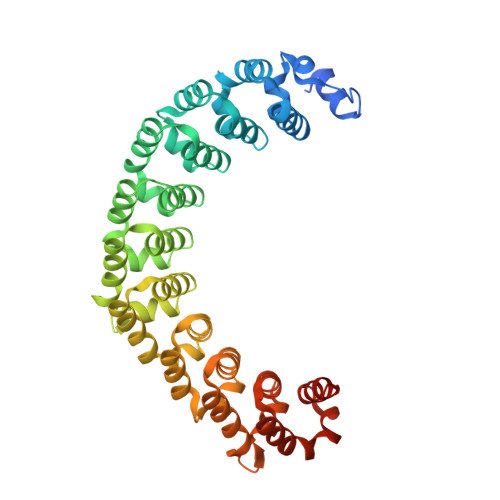Expanding RNA binding specificity and affinity of engineered PUF domains.
Zhao, Y.Y., Mao, M.W., Zhang, W.J., Wang, J., Li, H.T., Yang, Y., Wang, Z., Wu, J.W.(2018) Nucleic Acids Res 46: 4771-4782
- PubMed: 29490074
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky134
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5YKH, 5YKI - PubMed Abstract:
Specific manipulation of RNA is necessary for the research in biotechnology and medicine. The RNA-binding domains of Pumilio/fem-3 mRNA binding factors (PUF domains) are programmable RNA binding scaffolds used to engineer artificial proteins that specifically modulate RNAs. However, the native PUF domains generally recognize 8-nt RNAs, limiting their applications. Here, we modify the PUF domain of human Pumilio1 to engineer PUFs that recognize RNA targets of different length. The engineered PUFs bind to their RNA targets specifically and PUFs with more repeats have higher binding affinity than the canonical eight-repeat domains; however, the binding affinity reaches the peak at those with 9 and 10 repeats. Structural analysis on PUF with nine repeats reveals a higher degree of curvature, and the RNA binding unexpectedly and dramatically opens the curved structure. Investigation of the residues positioned in between two RNA bases demonstrates that tyrosine and arginine have favored stacking interactions. Further tests on the availability of the engineered PUFs in vitro and in splicing function assays indicate that our engineered PUFs bind RNA targets with high affinity in a programmable way.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Life Sciences, Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Protein Sciences, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China.