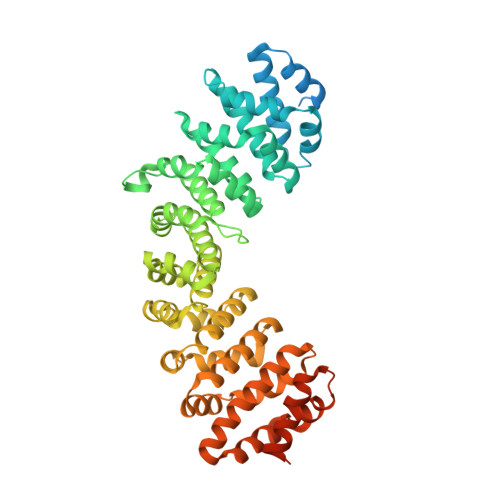
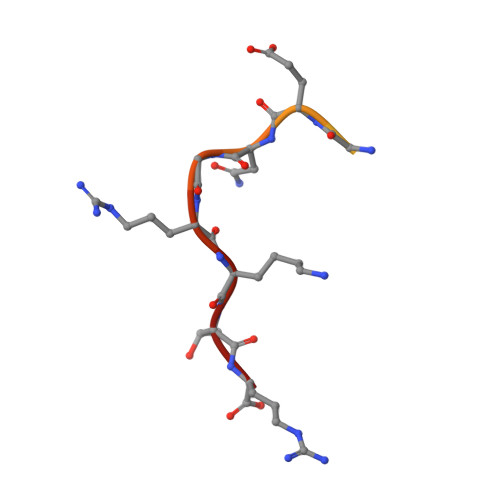
Synergy of two low-affinity NLSs determines the high avidity of influenza A virus nucleoprotein NP for human importin alpha isoforms.
Wu, W., Sankhala, R.S., Florio, T.J., Zhou, L., Nguyen, N.L.T., Lokareddy, R.K., Cingolani, G., Pante, N.(2017) Sci Rep 7: 11381-11381
- PubMed: 28900157
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11018-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5V5O, 5V5P - PubMed Abstract:
The influenza A virus nucleoprotein (NP) is an essential multifunctional protein that encapsidates the viral genome and functions as an adapter between the virus and the host cell machinery. NPs from all strains of influenza A viruses contain two nuclear localization signals (NLSs): a well-studied monopartite NLS1 and a less-characterized NLS2, thought to be bipartite. Through site-directed mutagenesis and functional analysis, we found that NLS2 is also monopartite and is indispensable for viral infection. Atomic structures of importin α bound to two variants of NLS2 revealed NLS2 primarily binds the major-NLS binding site of importin α, unlike NLS1 that associates with the minor NLS-pocket. Though peptides corresponding to NLS1 and NLS2 bind weakly to importin α, the two NLSs synergize in the context of the full length NP to confer high avidity for importin α7, explaining why the virus efficiently replicates in the respiratory tract that exhibits high levels of this isoform. This study, the first to functionally characterize NLS2, demonstrates NLS2 plays an important and unexpected role in influenza A virus infection. We propose NLS1 and NLS2 form a bipartite NLS in trans, which ensures high avidity for importin α7 while preventing non-specific binding to viral RNA.
Organizational Affiliation:
University of British Columbia, Department of Zoology, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T1Z4, Canada.