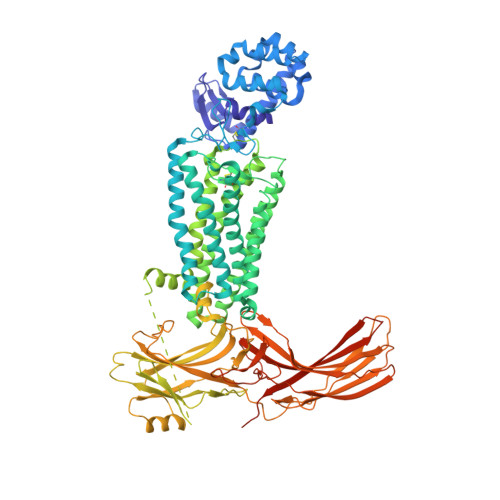
X-ray laser diffraction for structure determination of the rhodopsin-arrestin complex.
Zhou, X.E., Gao, X., Barty, A., Kang, Y., He, Y., Liu, W., Ishchenko, A., White, T.A., Yefanov, O., Han, G.W., Xu, Q., de Waal, P.W., Suino-Powell, K.M., Boutet, S., Williams, G.J., Wang, M., Li, D., Caffrey, M., Chapman, H.N., Spence, J.C., Fromme, P., Weierstall, U., Stevens, R.C., Cherezov, V., Melcher, K., Xu, H.E.(2016) Sci Data 3: 160021-160021
- PubMed: 27070998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.21
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5DGY - PubMed Abstract:
Serial femtosecond X-ray crystallography (SFX) using an X-ray free electron laser (XFEL) is a recent advancement in structural biology for solving crystal structures of challenging membrane proteins, including G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), which often only produce microcrystals. An XFEL delivers highly intense X-ray pulses of femtosecond duration short enough to enable the collection of single diffraction images before significant radiation damage to crystals sets in. Here we report the deposition of the XFEL data and provide further details on crystallization, XFEL data collection and analysis, structure determination, and the validation of the structural model. The rhodopsin-arrestin crystal structure solved with SFX represents the first near-atomic resolution structure of a GPCR-arrestin complex, provides structural insights into understanding of arrestin-mediated GPCR signaling, and demonstrates the great potential of this SFX-XFEL technology for accelerating crystal structure determination of challenging proteins and protein complexes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Structural Sciences, Center for Structural Biology and Drug Discovery, Van Andel Research Institute, Grand Rapids, Michigan 49503, USA.