[NiFe]-hydrogenases revisited: nickel-carboxamido bond formation in a variant with accrued O2-tolerance and a tentative re-interpretation of Ni-SI states.
Volbeda, A., Martin, L., Liebgott, P.P., De Lacey, A.L., Fontecilla-Camps, J.C.(2015) Metallomics 7: 710-718
- PubMed: 25780984
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c4mt00309h
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
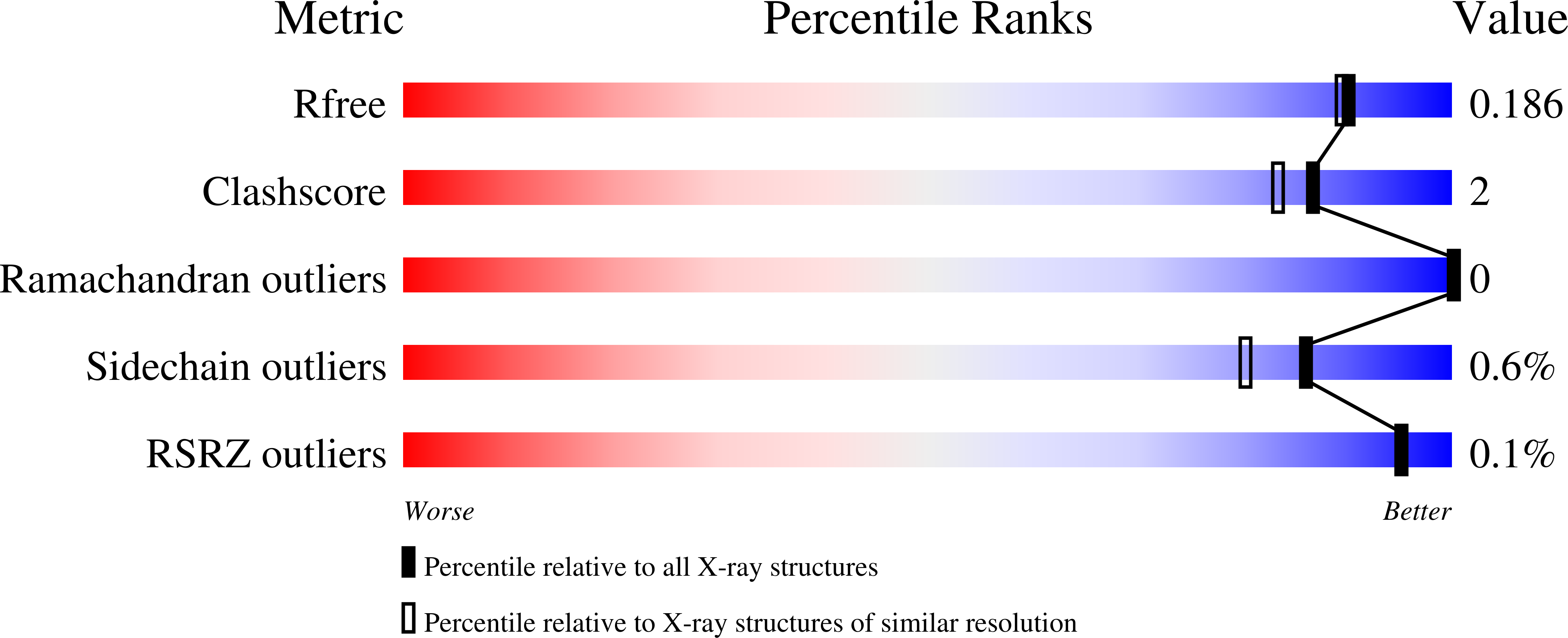
4UD2, 4UD6, 4UE2, 4UE6, 4UEQ, 4UEW - PubMed Abstract:
[NiFe]-hydrogenases are well-studied enzymes capable of oxidizing molecular hydrogen and reducing protons. EPR and FTIR spectroscopic studies have shown that these enzymes can be isolated in several redox states that include paramagnetic oxidized inactive Ni-A and Ni-B species and a reduced Ni-C form. The latter and the diamagnetic respectively more oxidized Ni-SI and more reduced Ni-R forms are generally thought to be involved in the catalytic cycle of [NiFe]-hydrogenases. With the exception of Ni-SI, these different stable states have been well characterized. Here, based on the crystal structure of a partially reduced Desulfovibrio fructosovorans (Df) enzyme and data from the literature we propose that at least one of the Ni-SI sub-states contains an unexpected combination of hydride and sulfenic acid moieties. We have also determined the structure of the less oxygen-sensitive Df [NiFe]-hydrogenase V74C mutant and found that more than half of the active site nickel occupies a novel position, called Ni'. In this new position, the metal ion is coordinated by two cysteine thiolates, a bridging species modeled as SH(-) and a main chain carboxamido N atom. The Ni' coordination is similar to the one found in Ni superoxide dismutase, an enzyme that operates at significantly more positive potentials than [NiFe]-hydrogenases. We propose that the oxygen-tolerance of the V74C variant results from a high potential stabilization of a Ni'(iii) species induced by the change in the metal ion coordination sphere. We also propose that transient Ni'(iii) species can rapidly attract successive electrons from the Fe4S4 proximal cluster accelerating the reduction of oxygen to water and hydroxide. The naturally occurring oxygen-tolerant [NiFe]-hydrogenases have an unusual proximal cluster that has been shown to be exceptionally plastic and capable of undergoing two successive one-electron oxidations. This double oxidation is modulated by the migration of one of the iron atoms in the cluster to the main chain where, as Fe(iii), it forms a bond with a carboxamido N ligand. Like in the Df V74C variant the electrons from the proximal cluster help reducing O2 to H2O and OH(-). In conclusion, in both cases a metal-carboxamido bond may explain, at least partially, the observed oxygen tolerance.
Organizational Affiliation:
CEA, IBS, F-38044 Grenoble, France. anne.volbeda@ibs.fr juan.fontecilla@ibs.fr.