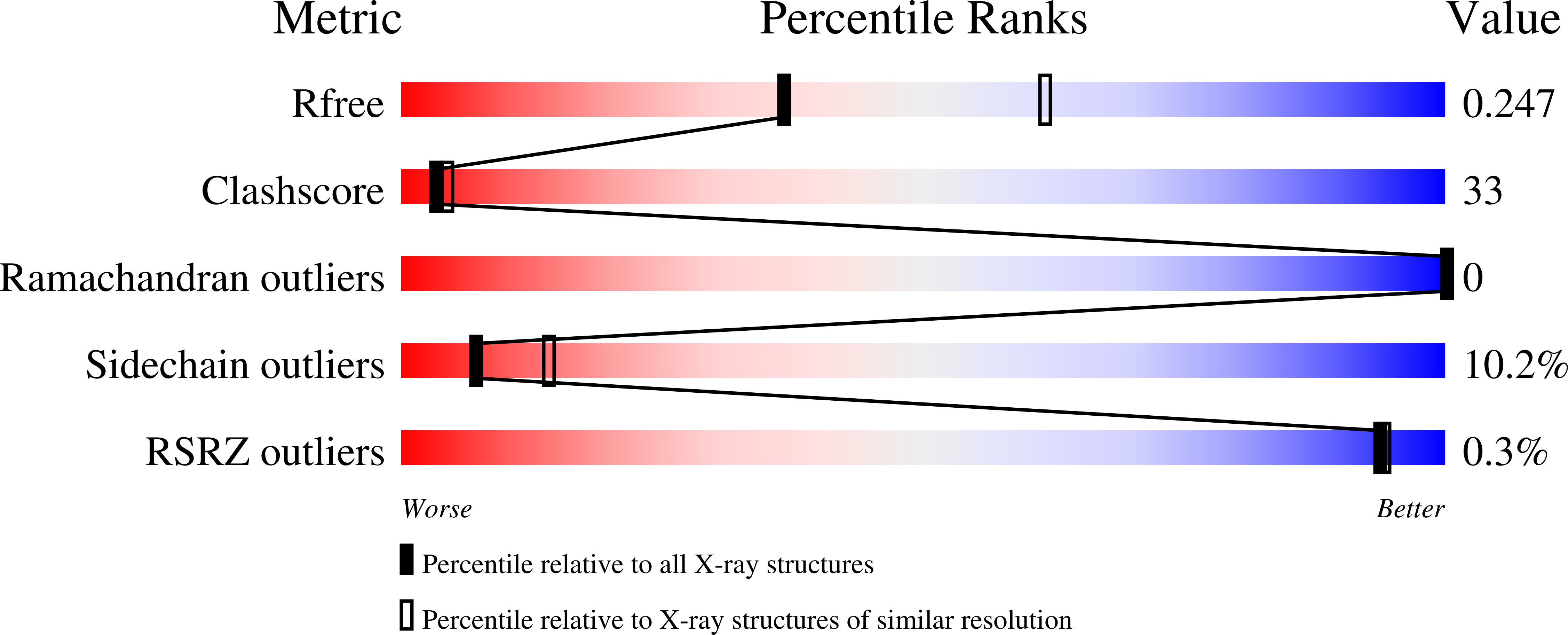
A Structurally Dynamic N-terminal Helix Is a Key Functional Determinant in Staphylococcal Complement Inhibitor (SCIN) Proteins.
Garcia, B.L., Summers, B.J., Ramyar, K.X., Tzekou, A., Lin, Z., Ricklin, D., Lambris, J.D., Laity, J.H., Geisbrecht, B.V.(2013) J Biol Chem 288: 2870-2881
- PubMed: 23233676
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.426858
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4H6H, 4H6I - PubMed Abstract:
Complement is a network of interacting circulatory and cell surface proteins that recognizes, marks, and facilitates clearance of microbial invaders. To evade complement attack, the pathogenic organism Staphylococcus aureus expresses a number of secreted proteins that interfere with activation and regulation of the complement cascade. Staphylococcal complement inhibitors (SCINs) are one important class of these immunomodulators and consist of three active members (SCIN-A/-B/-C). SCINs inhibit a critical enzymatic complex, the alternative pathway C3 convertase, by targeting a functional "hot spot" on the central opsonin of complement, C3b. Although N-terminal truncation mutants of SCINs retain complement inhibitory properties, they are significantly weaker binders of C3b. To provide a structural basis for this observation, we undertook a series of crystallographic and NMR dynamics studies on full-length SCINs. This work reveals that N-terminal SCIN domains are characterized by a conformationally dynamic helical motif. C3b binding and functional experiments further demonstrate that this sequence-divergent N-terminal region of SCINs is both functionally important and context-dependent. Finally, surface plasmon resonance data provide evidence for the formation of inhibitor·enzyme·substrate complexes ((SCIN·C3bBb)·C3). Similar to the (SCIN·C3bBb)(2) pseudodimeric complexes, ((SCIN·C3bBb)·C3) interferes with the interaction of complement receptors and C3b. This activity provides an additional mechanism by which SCIN couples convertase inhibition to direct blocking of phagocytosis. Together, these data suggest that tethering multi-host protein complexes by small modular bacterial inhibitors may be a global strategy of immune evasion used by S. aureus. The work presented here provides detailed structure-activity relationships and improves our understanding of how S. aureus circumvents human innate immunity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Cell Biology and Biophysics, School of Biological Sciences, University of Missouri, Kansas City, Missouri 64110, USA.